
Summary
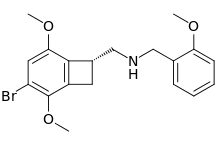
2CBCB-NBOMe (NBOMe-TCB-2) is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine series of hallucinogens, which was discovered in 2007 at Purdue University as part of the ongoing research program of the team led by David Nichols focusing on the mapping of the specific amino acid residues responsible for ligand binding to the 5HT2A receptor. 2CBCB-NBOMe acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors, with a Ki of 0.27 nM at the human 5-HT2A receptor, a similar potency to other agonists such as TCB-2, NBOMe-2C-I and Bromo-DragonFLY.[1]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H22BrNO3 |
| Molar mass | 392.293 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
| | |
Analogues and derivatives edit
Analogues and derivatives of 2C-B:
25-N:
- 25B-N1POMe
- 25B-NAcPip
25-NM:
- 25B-NMe7BF
- 25B-NMe7BT
- 25B-NMe7Bim
- 25B-NMe7Box
- 25B-NMe7DHBF
- 25B-NMe7Ind
- 25B-NMe7Indz
- 25B-NMePyr
- 2C-B-FLY
- 2CBFly-NBOMe (NBOMe-2CB-Fly)
- DOB-FLY
- DOB-2-DRAGONFLY-5-BUTTERFLY
Other:
Legality edit
United Kingdom edit
This substance is a Class A drug in the United Kingdom as a result of the N-benzylphenethylamine catch-all clause in the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971.[6]
United States edit
2CBCB-NBOMe is a controlled substance in Vermont as of January 2016.[7]
References edit
- ^ Braden MR (2007). Towards a biophysical understanding of hallucinogen action (Ph.D.). Purdue University. ProQuest 304838368.
- ^ "Explore N-(2C-B)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ^ "Explore N-(2C-FLY)-Fentanyl | PiHKAL · info". isomerdesign.com.
- ^ Glennon, Richard A.; Bondarev, Mikhail L.; Khorana, Nantaka; Young, Richard; May, Jesse A.; Hellberg, Mark R.; McLaughlin, Marsha A.; Sharif, Najam A. (November 2004). "β-Oxygenated Analogues of the 5-HT2ASerotonin Receptor Agonist 1-(4-Bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-aminopropane". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 47 (24): 6034–6041. doi:10.1021/jm040082s. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 15537358.
- ^ Beta-hydroxyphenylalkylamines and their use for treating glaucoma
- ^ "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Ketamine etc.) (Amendment) Order 2014". UK Statutory Instruments 2014 No. 1106. www.legislation.gov.uk.
- ^ "Regulated Drugs Rule" (PDF). Vermont Department of Health. Retrieved 14 October 2015.


