
Summary
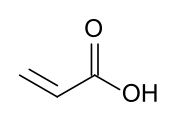
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: propenoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCOOH. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than a million tons are produced annually.[6]
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Acrylic acid[2]
| |
| Preferred IUPAC name
Prop-2-enoic acid[2] | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 635743 | |
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.071 |
| EC Number |
|
| 1817 | |
| KEGG |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H4O2 | |
| Molar mass | 72.063 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless liquid |
| Odor | Acrid[3] |
| Density | 1.051 g/mL |
| Melting point | 14 °C (57 °F; 287 K) |
| Boiling point | 141 °C (286 °F; 414 K) |
| Miscible | |
| log P | 0.28[4] |
| Vapor pressure | 3 mmHg[3] |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.25 (H2O)[5] |
| Viscosity | 1.3 cP at 20 °C (68 °F) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
    
| |
| Danger | |
| H226, H302, H312, H314, H332, H400 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P302+P352, P303+P361+P353, P304+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P312, P321, P322, P330, P363, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | 68 °C (154 °F; 341 K) |
| 429 °C (804 °F; 702 K) | |
| Explosive limits | 2.4–8.02%[3] |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
None[3] |
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 2 ppm (6 mg/m3) [skin][3] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
N.D.[3] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
acrylate |
Related carboxylic acids
|
acetic acid propionic acid lactic acid 3-hydroxypropionic acid malonic acid butyric acid crotonic acid |
Related compounds
|
allyl alcohol propionaldehyde acrolein methyl acrylate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
History edit
The word "acrylic" was coined in 1843, for a chemical derivative of acrolein, an acrid-smelling oil derived from glycerol.
Production edit
Acrylic acid is produced by oxidation of propylene, which is a byproduct of the production of ethylene and gasoline:
- 2 CH2=CHCH3 + 3 O2 → 2 CH2=CHCO2H + 2 H2O
Historical methods edit
Because acrylic acid and its esters have long been valued commercially, many other methods have been developed. Most have been abandoned for economic or environmental reasons. An early method was the hydrocarboxylation of acetylene ("Reppe chemistry"):
This method requires nickel carbonyl, high pressures of carbon monoxide, and acetylene, which is relatively expensive compared to propylene.
Acrylic acid was once manufactured by the hydrolysis of acrylonitrile, a material derived from propene by ammoxidation, but this route was abandoned because it cogenerates ammonium side products, which must be disposed of. Other now abandoned precursors to acrylic acid include ethenone and ethylene cyanohydrin.[6]
Research edit
Propane is a much cheaper raw material than propylene, so an alternative route being explored is the one-step selective oxidation of propane.[7]
Carboxylating ethylene to acrylic acid under supercritical carbon dioxide is thermodynamically possible, but efficient catalysts have not been developed.[8] 3-Hydroxypropionic acid (3HP), an acrylic-acid precursor by dehydration, can be produced from sugars, but the process is not competitive.[9][10]
Reactions and uses edit
Acrylic acid undergoes the typical reactions of a carboxylic acid. When reacted with an alcohol, it forms the corresponding ester. The esters and salts of acrylic acid are collectively known as acrylates (or propenoates). The most common alkyl esters of acrylic acid are methyl, butyl, ethyl, and 2-ethylhexyl acrylate.
Acrylic acid and its esters readily combine with themselves (to form polyacrylic acid) or other monomers (e.g. acrylamides, acrylonitrile, vinyl compounds, styrene, and butadiene) by reacting at their double bond, forming homopolymers or copolymers, which are used in the manufacture of various plastics, coatings, adhesives, elastomers, as well as floor polishes and paints.
Acrylic acid is used in many industries, including the diaper industry, the water treatment industry, and the textiles industry. The annual worldwide consumption of acrylic acid is projected to reach more than an estimated 8,000 kilotons by 2020. This increase is expected due to its use in new applications, including personal care products, detergents, and products for adult incontinence.[11]
Substituents edit
As a substituent acrylic acid can be found as an acyl group or a carboxyalkyl group, depending on the removal of the group from the molecule.
More specifically, these are:
- The acryloyl group, with the removal of the −OH from carbon-1.
- The 2-carboxyethenyl group, with the removal of a −H from carbon-3. This substituent group is found in chlorophyll.
Safety edit
Acrylic acid is severely irritating and corrosive to the skin and the respiratory tract. Eye contact can result in severe and irreversible injury. Low exposure will cause minimal or no health effects, while high exposure could result in pulmonary edema. The LD50 is 340 mg/kg (rat, oral) with the lowest recorded LD50 being 293 mg/kg (oral, rat) comparable to ethylene glycol which is indicative of being a potent poison.[12] Ethyl acrylate was once used as synthetic food flavoring and was withdrawn by FDA possibly due to cancerogenic effects observed in lab animals.[13]
Animal studies showed that high-doses of acrylic acid decreased weight gain. Acrylic acid can be converted to non-toxic lactic acid.[14]
Acrylic acid is a constituent of tobacco smoke.[15]
See also edit
References edit
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 124.
- ^ a b International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 746. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b c d e f NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0013". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "Acrylic acid_msds".
- ^ Dippy, J. F. J.; Hughes, S. R. C.; Rozanski, A. (1959). "The dissociation constants of some symmetrically disubstituted succinic acids". Journal of the Chemical Society: 2492–2498. doi:10.1039/JR9590002492.
- ^ a b Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Takahisa; Shimizu, Noboru; Prescher, Günter; Schwind, Helmut; Weiberg, Otto; Marten, Klaus; Greim, Helmut (2003). "Acrylic Acid and Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_161.pub2. ISBN 978-3527306732.
- ^ Védrine, Jacques (2017-11-10). "Heterogeneous Catalysis on Metal Oxides". Catalysts. 7 (11). MDPI AG: 341. doi:10.3390/catal7110341. ISSN 2073-4344.
- ^ Sakakura, Toshiyasu; Choi, Jun-Chul; Yasuda, Hiroyuki (13 June 2007). "Transformation of Carbon dioxide". Chemical Reviews. 107 (6): 2365–2387. doi:10.1021/cr068357u. PMID 17564481.
- ^ Sweet Deal: Dow and Partner Cook up Sugar-to-Acrylic Plan. Durabilityanddesign.com. Retrieved on 2012-05-24.
- ^ Better Bugs to Make Plastics, Technology Review, September 20, 2010, retrieved January 9, 2012. Technologyreview.com (2010-09-20). Retrieved on 2012-05-24.
- ^ "Acrylic acid market". Retrieved 2018-05-30.
- ^ "Webwiser Acrylic Acid".
- ^ "Synthetic food flavorings law update".
- ^ "Provisional Peer-Reviewed Toxicity Values for Acrylic Acid" (PDF). www.google.com. Retrieved 2022-04-29.
- ^ Talhout, Reinskje; Schulz, Thomas; Florek, Ewa; Van Benthem, Jan; Wester, Piet; Opperhuizen, Antoon (2011). "Hazardous Compounds in Tobacco Smoke". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 8 (12): 613–628. doi:10.3390/ijerph8020613. ISSN 1660-4601. PMC 3084482. PMID 21556207.
External links edit
- National Pollutant Inventory: Acrylic acid
- CDC – NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards – Acrylic acid



