
KNOWPIA
WELCOME TO KNOWPIA
Summary
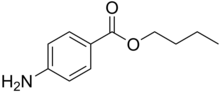
Butamben is a local anesthetic. Proprietary names includes Alvogil in Spain and Alvogyl in Switzerland. It is one of three components in the topical anesthetic Cetacaine.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | n-butyl p-aminobenzoate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.107 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H15NO2 |
| Molar mass | 193.246 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
| Melting point | 58 °C (136 °F) |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Chemistry edit
It is the ester of 4-aminobenzoic acid and butanol.[1] A white, odourless, crystalline powder. that is mildly soluble in water (1 part in 7000) and soluble in alcohol, ether, chloroform, fixed oils, and dilute acids. It slowly hydrolyses when boiled with water. Synonyms include Butamben, Butilaminobenzoato, and Butoforme.
Synthesis edit
The esterification between 4-Nitrobenzoic acid [62-23-7] (1) and 1-Butanol [71-36-3] (2) gives Butyl 4-Nitrobenzoate [120-48-9] (3). Bechamp reduction then gives Butamben (4).
Alternatively, 4-aminobenzoic acid can be used directly.
References edit
- ^ drugs.com Butamben
- ^ GB 148743, "Manufacture of normal butyl paramino benzoate", issued 1920, assigned to Ste Chim Usines Rhone.
- ^ US 1440652, Adams R, Volwiler E, issued 1923, assigned to Abbott Labs.
- ^ Morogina OK, Nasibulin AA, Klyuev MV (1998). "Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation of p-Nitrobenzoic Acid Esters on Palladium Catalysts". Petroleum Chemistry. 38 (4): 251–255.
- ^ Hosangadi BD, Dave RH (August 1996). "An efficient general method for esterification of aromatic carboxylic acids". Tetrahedron Letters. 37 (35): 6375–6378. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(96)01351-2.
- ^ Gök Y, Alici B, Cetinkaya E, Özdemir İ, Özeroğlu Ö (2010). "Ionic liquids as solvent for efficient esterification of carboxylic acids with alkyl halides". Turkish Journal of Chemistry. 34 (2): 187–192. doi:10.3906/kim-0904-39. S2CID 93020800.
- ^ Matsunaga Y, Sakamoto S, Togashi A, Tsujimoto M (July 1994). "Smectogenic Salts Formed by Combination of Alkyl p-Aminobenzoates and p-Ethyl-or p-Chlorobenzenesulfonic Acid". Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals Science and Technology. Section A. Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals. 250 (1): 161–166. doi:10.1080/10587259408028202.
- ^ Brill HC (June 1921). "Esters of Aminobenzoic Acids". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 43 (6): 1320–1323. doi:10.1021/ja01439a014.


