
Summary
The Campylobacterales are an order of Campylobacterota which make up the epsilon subdivision, together with the small family Nautiliaceae. They are Gram-negative. Most of the species are microaerophilic.[1]
| Campylobacterales | |
|---|---|
| |
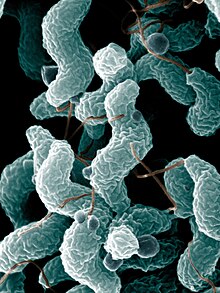
| Campylobacter jejuni bacteria | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Phylum: | Campylobacterota |
| Class: | "Campylobacteria" Waite et al. 2017 |
| Order: | Campylobacterales Garrity et al. 2006 |
| Families and genera | |
| |
Molecular signatures edit
Comparative genomic analysis has led to the identification of 49 proteins which are uniquely found in virtually all species of the order Campylobacterales. Additionally, two conserved signature indels have been identified which, along with the proteins, serve as molecular markers for the order. The indels are a three-amino-acid insertion in the B protein of the Uvr ABC system, and a two-amino-acid deletion in phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase.[2]
Phylogeny edit
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)[3] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI)[4]
| 16S rRNA based LTP_08_2023[5][6][7] | 120 single copy marker proteins based GTDB 08-RS214[8][9][10] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Unassigned genera:
- "Flexispira" Bryner 1987
- "Candidatus Thioturbo" Muyzer et al. 2005
- "Thiofractor" Makita et al. 2012
- "Thiobarbaceae" Assié et al. 2020
- "Candidatus Thiobarba" Assié et al. 2020
See also edit
References edit
- ^ Garrity, George M.; Brenner, Don J.; Krieg, Noel R.; Staley, James T. (eds.) (2005). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume Two: The Proteobacteria, Part C: The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteobacteria. New York, New York: Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-24145-6.
- ^ Gupta, R. S. (2006). Molecular signatures (unique proteins and conserved indels) that are specific for the epsilon proteobacteria. BMC Genomics. 7:167.
- ^ A.C. Parte; et al. "Campylobacterales". List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN). Retrieved 2023-09-09.
- ^ Sayers; et al. "Campylobacterales". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. Retrieved 2023-09-09.
- ^ "The LTP". Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ "LTP_all tree in newick format". Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ "LTP_08_2023 Release Notes" (PDF). Retrieved 20 November 2023.
- ^ "GTDB release 08-RS214". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "bac120_r214.sp_label". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Taxon History". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 10 May 2023.


