
KNOWPIA
WELCOME TO KNOWPIA
Summary
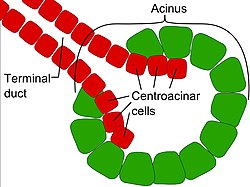
Centroacinar cells are spindle-shaped cells in the exocrine pancreas. They represent an extension of the intercalated duct into each pancreatic acinus.[1] These cells are commonly known as duct cells, and secrete an aqueous bicarbonate solution under stimulation by the hormone secretin. They also secrete mucin.
| Centroacinar cell | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Location | Pancreas |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | cellula centroacinosa |
| TH | H3.04.07.0.00008 |
| Anatomical terms of microanatomy [edit on Wikidata] | |
The intercalated ducts take the bicarbonate to intralobular ducts which become lobular ducts. These lobular ducts finally converge to form the main pancreatic duct.[1]
See also edit
References edit
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1204 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links edit
- Anatomy Atlases – Microscopic Anatomy, plate 10.213 - "Pancreas"
- Histology image: 10406loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University - "Liver, Gall Bladder, and Pancreas: pancreas, centroacinar cells"
- UIUC Histology Subject 870


