
Summary
A clathrate is a chemical substance consisting of a lattice that traps or contains molecules. The word clathrate is derived from the Latin clathratus (clatratus), meaning 'with bars, latticed'.[1] Most clathrate compounds are polymeric and completely envelop the guest molecule, but in modern usage clathrates also include host–guest complexes and inclusion compounds.[2] According to IUPAC, clathrates are inclusion compounds "in which the guest molecule is in a cage formed by the host molecule or by a lattice of host molecules."[3] The term refers to many molecular hosts, including calixarenes and cyclodextrins and even some inorganic polymers such as zeolites.
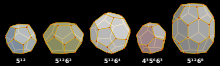
Clathrates can be divided into two categories: clathrate hydrates and inorganic clathrates. Each clathrate is made up of a framework and guests that reside the framework. Most common clathrate crystal structures can be composed of cavities such as dodecahedral, tetrakaidecahedral, and hexakaidecahedral cavities.
The molar fraction of water of most clathrate hydrates is 85%. Clathrate hydrates are derived from organic hydrogen-bonded frameworks. These frameworks are prepared from molecules that "self-associate" by multiple hydrogen-bonding interactions. Small molecules or gases (i.e. methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen) can be encaged as a guest in hydrates. The ideal guest/host ratio for clathrate hydrates range from 0.8 to 0.9. The guest interaction with the host is limited to van der Waals forces. Certain exceptions exist in semiclathrates where guests incorporate into the host structure via hydrogen bonding with the host structure. Hydrates form often with partial guest filling and collapse in the absence of guests occupying the water cages. Like ice, clathrate hydrates are stable at low temperatures and high pressure and possess similar properties like electrical resistivity. Clathrate hydrates are naturally occurring and can be found in the permafrost and oceanic sediments. Hydrates can also be synthesized through seed crystallization or using amorphous precursors for nucleation.[4]
Unlike hydrates, inorganic clathrates have a covalently bonded framework of inorganic atoms with guests typically consisting of alkali or alkaline earth metals. Due to the stronger covalent bonding, the cages are often smaller than hydrates. Guest atoms interact with the host by ionic or covalent bonds. Therefore, partial substitution of guest atoms follow Zintl rules so that the charge of the overall compound is conserved. Most inorganic clathrates have full occupancy of its framework cages by a guest atom to be in stable phase. Inorganic clathrates can be synthesized by direct reaction using ball milling at high temperatures or high pressures. Crystallization from melt in another common synthesis route. Due to the wide variety of composition of host and guest species, inorganic clathrates are much more chemically diverse and possess a wide range of properties. Most notably, inorganic clathrates can be found to be both an insulator and a superconductor (Ba8Si46). A common property of inorganic clathrates that has attracted researchers is low thermal conductivity. Low thermal conductivity is attributed to the ability of the guest atom to "rattle" within the host framework. The freedom of movement of the guest atoms scatters phonons that transport heat.[4]

Examples edit
Clathrates have been explored for many applications including: gas storage, gas production, gas separation, desalination, thermoelectrics, photovoltaics, and batteries.
- Clathrate compounds with formula A8B16X30, where A is an alkaline earth metal, B is a group III element, and X is an element from group IV have been explored for thermoelectric devices. Thermoelectric materials follow a design strategy called the phonon glass electron crystal concept.[6][7] Low thermal conductivity and high electrical conductivity is desired to produce the Seebeck Effect. When the guest and host framework are appropriately tuned, clathrates can exhibit low thermal conductivity, i.e., phonon glass behavior, while electrical conductivity through the host framework is undisturbed allowing clathrates to exhibit electron crystal.
- Methane clathrates feature the hydrogen-bonded framework contributed by water and the guest molecules of methane. Large amounts of methane naturally frozen in this form exist both in permafrost formations and under the ocean sea-bed.[8] Other hydrogen-bonded networks are derived from hydroquinone, urea, and thiourea. A much studied host molecule is Dianin's compound.
- Hofmann clathrates are coordination polymers with the formula Ni(CN)4·Ni(NH3)2(arene). These materials crystallize with small aromatic guests (benzene, certain xylenes), and this selectivity has been exploited commercially for the separation of these hydrocarbons.[2] Metal organic frameworks (MOFs) form clathrates.
History edit
Clathrate hydrates were discovered in 1810 by Humphry Davy.[9] Clathrates were studied by P. Pfeiffer in 1927 and in 1930, E. Hertel defined "molecular compounds" as substances decomposed into individual components following the mass action law in solution or gas state. Clathrate hydrates were discovered to form blockages in gas pipelines in 1934 by Hammerschmidt that led to increase in research to avoid hydrate formation.[10] In 1945, H. M. Powell analyzed the crystal structure of these compounds and named them clathrates. Gas production through methane hydrates has since been realized and has been tested for energy production in Japan and China.[4]
Related materials edit
Inclusion compounds are often molecules, whereas clathrates are typically polymeric[citation needed]. Intercalation compounds are not 3-dimensional, unlike clathrate compounds. Photolytically-sensitive caged compounds have been examined as containers for releasing a drug or reagent.[11]
Zeolites are another type of crystalline structures that form a framework with cavities in which guest species can reside. Unlike clathrates, zeolites are defined by the tetrahedra linking of four oxygen atoms surrounding a cation.[citation needed] The guests are also not required to fill the open cavities. Zeolite structures are defined by the diverse building units of the framework, as opposed to cavity structures in clathrates. Similar applications have been explored.
Silica clathrasil are compounds structurally similar to clathrate hydrates with a SiO2 framework and can be found in a range of marine sediment.[12]
See also edit
References edit
- ^ Latin dictionary Archived 2012-04-14 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Atwood, J. L. (2012) "Inclusion Compounds" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a14_119
- ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "clathrates". doi:10.1351/goldbook.C01097
- ^ a b c d e Krishna, Lakshmi; Koh, Carolyn A. (February 2015). "Inorganic and methane clathrates: Versatility of guest–host compounds for energy harvesting". MRS Energy & Sustainability. 2 (1): 8. doi:10.1557/mre.2015.9. ISSN 2329-2229.
- ^ Birchall, T.; Frampton, C. S.; Schrobilgen, G. J.; Valsdóttir, J. (1989). "Β-Hydroquinone xenon clathrate". Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications. 45 (6): 944–946. Bibcode:1989AcCrC..45..944B. doi:10.1107/S0108270188014556.
- ^ Nolas, G. S.; Cohn, J. L.; Slack, G. A.; Schujman, S. B. (1998-07-13). "Semiconducting Ge clathrates: Promising candidates for thermoelectric applications". Applied Physics Letters. 73 (2): 178–180. Bibcode:1998ApPhL..73..178N. doi:10.1063/1.121747. ISSN 0003-6951.
- ^ Beekman, M., Morelli, D. T., Nolas, G. S. (2015). "Better thermoelectrics through glass-like crystals". Nature Materials. 14 (12): 1182–1185. Bibcode:2015NatMa..14.1182B. doi:10.1038/nmat4461. ISSN 1476-4660. PMID 26585077.
- ^ Pearce, Fred (27 June 2009). "Ice on fire: The next fossil fuel". New Scientist. No. 2714. pp. 30–33. Archived from the original on April 13, 2016. Retrieved July 5, 2009.
- ^ Thomas, Ellen (November 2004). "Clathrates: little known components of the global carbon cycle". Wesleyan University. Retrieved 13 December 2007.
- ^ Hammerschmidt, E. G. (1934-08-01). "Formation of Gas Hydrates in Natural Gas Transmission Lines". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry. 26 (8): 851–855. doi:10.1021/ie50296a010. ISSN 0019-7866.
- ^ Ellis-Davies, Graham C. R. (2007). "Caged compounds: Photorelease technology for control of cellular chemistry and physiology". Nature Methods. 4 (8): 619–628. doi:10.1038/nmeth1072. PMC 4207253. PMID 17664946.
- ^ Momma, Koichi; Ikeda, Takuji; Nishikubo, Katsumi; Takahashi, Naoki; Honma, Chibune; Takada, Masayuki; Furukawa, Yoshihiro; Nagase, Toshiro; Kudoh, Yasuhiro (September 2011). "New silica clathrate minerals that are isostructural with natural gas hydrates". Nature Communications. 2 (1): 196. Bibcode:2011NatCo...2..196M. doi:10.1038/ncomms1196. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 21326228.


