
Summary
Proteins that bind cyclic nucleotides (cAMP or cGMP) share a structural domain of about 120 residues. The best studied of these proteins is the prokaryotic catabolite gene activator (also known as the cAMP receptor protein) (gene crp) where such a domain is known to be composed of three alpha-helices and a distinctive eight-stranded, antiparallel beta-barrel structure. There are six invariant amino acids in this domain, three of which are glycine residues that are thought to be essential for maintenance of the structural integrity of the beta-barrel. cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases (cAPK and cGPK) contain two tandem copies of the cyclic nucleotide-binding domain. The cAPK's are composed of two different subunits, a catalytic chain and a regulatory chain, which contains both copies of the domain. The cGPK's are single chain enzymes that include the two copies of the domain in their N-terminal section. Vertebrate cyclic nucleotide-gated ion-channels also contain this domain. Two such cations channels have been fully characterized, one is found in rod cells where it plays a role in visual signal transduction.
| Cyclic nucleotide-binding domain | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
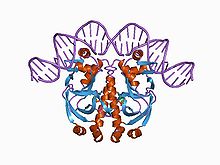 Structure of a CAP-DNA complex.[1] | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | cNMP_binding | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF00027 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR000595 | ||||||||||
| SMART | SM00100 | ||||||||||
| PROSITE | PDOC00691 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1cgp / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| CDD | cd00038 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
Human proteins containing this domain edit
CNBD1; CNGA1; CNGA2; CNGA3; CNGB1; CNGB3; HCN1; HCN2; HCN3; HCN4; KCNH1; KCNH2; KCNH3; KCNH4; KCNH5; KCNH6; KCNH7; KCNH8; PNPLA6; PNPLA7; PRKAR1A; PRKAR1B; PRKAR2A; PRKAR2B; PRKG1; PRKG2; RAPGEF2; RAPGEF3; RAPGEF4; RAPGEF6; RCNC2; SLC9A10; SLC9A11;


