
KNOWPIA
WELCOME TO KNOWPIA
Summary
E-6801 is a partial agonist of the 5-HT6 receptor.[1] It enhanced recognition memory and reversed the memory deficits of scopolamine in an object recognition task in a rat model.[2] The mechanism of memory enhancement is due to a combined modulation of cholinergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
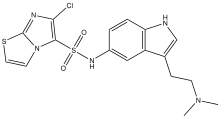
| Preferred IUPAC name
6-Chloro-N-{3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-5-yl}imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazole-5-sulfonamide | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H18ClN5O2S2 | |
| Molar mass | 423.94 g mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
See also edit
References edit
- ^ Romero, G. (August 2006). "Efficacy of selective 5-HT6 receptor ligands determined by monitoring 5-HT6 receptor-mediated cAMP signaling pathways". British Journal of Pharmacology. 148 (8): 1133–43. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0706827. PMC 1752021. PMID 16865095.
- ^ Kendall, I. (February 2011). "E-6801, a 5-HT6 receptor agonist, improves recognition memory by combined modulation of cholinergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission in the rat". Psychopharmacology. 213 (2–3): 413–30. doi:10.1007/s00213-010-1854-3. PMID 20405281. S2CID 10116984.


