
Summary
Haida /ˈhaɪdə/[2] (X̱aat Kíl, X̱aadas Kíl, X̱aayda Kil, Xaad kil[3]) is the language of the Haida people, spoken in the Haida Gwaii archipelago off the coast of Canada and on Prince of Wales Island in Alaska. An endangered language, Haida currently[when?] has 24 native speakers, though revitalization efforts are underway. At the time of the European arrival at Haida Gwaii in 1774, it is estimated that Haida speakers numbered about 15,000. Epidemics soon led to a drastic reduction in the Haida population, which became limited to three villages: Masset, Skidegate, and Hydaburg. Positive attitudes towards assimilation combined with the ban on speaking Haida in residential schools led to a sharp decline in the use of the Haida language among the Haida people, and today almost all ethnic Haida use English to communicate.
| Haida | |
|---|---|
| X̱aat Kíl, X̱aadas Kíl, X̱aayda Kil, Xaad kil | |
 A woman hangs posters with the Haida words for various body parts | |
| Native to | |
| Ethnicity | Haida people |
Native speakers | 13 (2018, 2020)[1] |
| Latin | |
| Official status | |
Official language in | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-2 | hai |
| ISO 639-3 | hai – inclusive codeIndividual codes: hdn – Northern Haidahax – Southern Haida |
| Glottolog | haid1248 |
| ELP | Xaad Kil (Haida) |
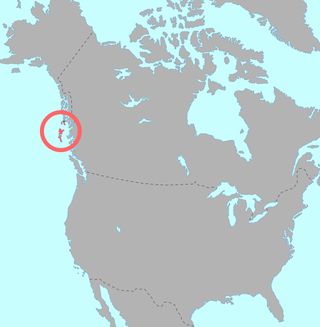 Pre-contact distribution of Haida | |
 Northern Haida is classified as Critically Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger | |
| People | Haida |
|---|---|
| Language | Haida kil |
| Country | Haida Gwaii |
Classification of the Haida language is a matter of controversy, with some linguists placing it in the Na-Dené language family and others arguing that it is a language isolate. Haida itself is split between Northern and Southern dialects, which differ primarily in phonology. The Northern Haida dialects have developed pharyngeal consonants, typologically uncommon sounds which are also found in some of the nearby Salishan and Wakashan languages.
The Haida sound system includes ejective consonants, glottalized sonorants, contrastive vowel length, and phonemic tone. The nature of tone differs between the dialects, and in Alaskan Haida it is primarily a pitch accent system. Syllabic laterals appear in all dialects of Haida, but are only phonemic in Skidegate Haida. Extra vowels which are not present in Haida words occur in nonsense words in Haida songs. There are a number of systems for writing Haida using the Latin alphabet, each of which represents the sounds of Haida differently.
While in Haida nouns and verbs behave as clear word classes, adjectives form a subclass of verbs. Haida has only a few adpositions. Indo-European-type adjectives translate into verbs in Haida, for example 'láa "(to be) good", and English prepositional phrases are usually expressed with Haida "relational nouns", for instance Alaskan Haida dítkw 'side facing away from the beach, towards the woods'. Haida verbs are marked for tense, aspect, mood, and evidentiality, and person is marked by pronouns that are cliticized to the verb. Haida also has hundreds of classifiers. Haida has the rare direct-inverse verbal alignment where instead of nominal cases, it is marked whether the grammatical subject and object follow or not a hierarchy between persons and noun classes. Haida also has obligatory possession, where certain types of nouns cannot stand alone and require a possessor.
History edit
The first documented contact between the Haida and Europeans was in 1772, on Juan Pérez's exploratory voyage.[4] At this time Haidas inhabited the Haida Gwaii, Dall Island, and Prince of Wales Island.[4] The precontact Haida population was about 15,000; the first smallpox epidemic came soon after initial contact, reducing the population to about 10,000 and depopulating a large portion of the Ninstints dialect area.[5] The next epidemic came in 1862, causing the population to drop to 1,658.[5] Venereal disease and tuberculosis further reduced the population to 588 by 1915.[5] This dramatic decline led to the merger of villages, the final result being three Haida villages: Masset (merged 1876), Skidegate (merged 1879), and Hydaburg (merged 1911).[6]
In the 1830s a pidgin trade language based on Haida, known as Haida Jargon, was used in the islands by speakers of English, Haida, Coast Tsimshian, and Heiltsuk.[7] The Fraser Canyon Gold Rush of 1858 led to a boom in the town of Victoria, and Southern Haida began traveling there annually, mainly for the purpose of selling their women.[8] For this the Haida used Chinook Jargon.[9] This contact with whites had a strong effect on the Southern Haida, even as the Northern Haida remained culturally conservative.[9] For instance, Skidegate Haida were reported as dressing in the European fashion in 1866, while Northern Haida "were still wearing bearskins and blankets ten years later."[9]
In 1862, William Duncan, a British Anglican missionary stationed at Fort Simpson, took fifty Tsimshian converts and created a new model community, Metlakatla, in Alaska.[10] The new village was greatly successful, and throughout the Northwest coast the attitude spread that abandoning tradition would pave the way for a better life.[11] The Haida themselves invited missionaries to their community, the first arriving in 1876.[11] These missionaries initially worked in the Haida language.[11]
The Rev. John Henry Keen translated the Book of Common Prayer into Haida, published in 1899 in London by the Church Mission Society.[12][nb 1] The book of Psalms as well as 3 Gospels and Acts from the New Testament would also be translated into Haida.[11] However, negative attitudes towards the use of the Haida language were widespread among the Haida people, even in the fairly conservative village of Masset where Keen was located.[11] In an 1894 letter, Keen wrote:
These people would fain have their services etc. entirely in English. It has been by sheer determination that I now have the whole service (except hymns and canticles) in the vernacular.
— John Henry Keen, 1894 letter, quoted in Enrico (2003:6)
Beginning at the turn of the century, Haida began sending their children to residential schools.[11] This practice was most widespread among the Southern Haida; among the Northern Haida it was practiced by the more "progressive" families.[13] These schools strictly enforced a ban on the use of native languages, and played a major role in the decimation of native Northwest Coast languages.[13] The practice of Haida families using English to address children spread in Masset in the 1930s, having already been practiced in Skidegate, the rationale being that this would aid the children in their school education.[13] After this point few children were raised with Haida as a primary language.[13]
Status edit
Today most Haida do not speak the Haida language. The language is listed as "critically endangered" in UNESCO's Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger, with nearly all speakers elderly.[14][15] As of 2003, most speakers of Haida are between 70 and 80 years of age, though they speak a "considerably simplified" form of Haida, and comprehension of the language is mostly limited to persons above the age of 50. The language is rarely used even among the remaining speakers and comprehenders.[16]
The Haida have a renewed interest in their traditional culture, and are now funding Haida language programs in schools in the three Haida communities, though these have been ineffectual.[17] Haida classes are available in many Haida communities and can be taken at the University of Alaska Southeast in Juneau, Ketchikan, and Hydaburg.[15][18] A Skidegate Haida language app is available for iPhone, based on a "bilingual dictionary and phrase collection comprised of words and phrases archived at the online Aboriginal language database FirstVoices.com."[19]
In 2017 Kingulliit Productions was working on the first feature film to be acted entirely in Haida; the actors had to be trained to pronounce the lines correctly.[20] The film, entitled SGaawaay K’uuna ("Edge of the Knife"), was due to be released in the United Kingdom in April 2019. [21]
Classification edit
Franz Boas first suggested that Haida might be genetically related to the Tlingit language in 1894, and linguist Edward Sapir included Haida in the Na-Dené language family in 1915.[22] This position was later supported by others, including Swanton, Pinnow, and Greenberg and Ruhlen.[22] Today, however, many linguists regard Haida as a language isolate.[23] This theory is not universally accepted; for example, Enrico (2004) argues that Haida does in fact belong to the Na-Dené family, though early loanwords make the evidence problematic.[22] A proposal linking Na-Dené to the Yeniseian family of central Siberia finds no evidence for including Haida.[24]
Dialects edit
Haida has a major dialectal division between Northern and Southern dialects.[4] Northern Haida is split into Alaskan (or Kaigani) Haida and Masset (or North Graham Island) Haida.[4] Southern Haida was originally split into Skidegate Haida and Ninstints Haida, but Ninstints Haida is now extinct and is poorly documented.[4] The dialects differ in phonology and to some extent vocabulary; however, they are grammatically mostly identical.[15]
Northern Haida is notable for its pharyngeal consonants.[25] Pharyngeal consonants are rare among the world's languages, even in North America.[26] They are an areal feature of some languages in a small portion of Northwest America, in the Salishan and Wakashan languages as well as Haida.[25] The pharyngeal consonants of Wakashan and Northern Haida are known to have developed recently.[25]
Phonology edit
Consonants edit
| Bilabial | Alveolar | Postalveolar / Palatal |
Palatal~Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Glottal | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| central | lateral | ||||||||
| Plosive | plain1 | b̥ | d̥ | ɡ̊ | ɢ̥ | (ʕ̥)3 | ʔ | ||
| aspirated | tʰ | kʰ | qʰ | ||||||
| ejective | tʼ | kʼ | qʼ | ||||||
| Affricate | lenis | d̥͡ɮ̊ | d̥͡ʒ̊ | ||||||
| fortis | t͡ɬʰ | t͡ʃʰ 2 | |||||||
| ejective | t͡sʼ | t͡ɬʼ | |||||||
| Fricative | s | ɬ | x | χ | (ħ)3 | h | |||
| Nasal | plain | m | n | ŋ | |||||
| glottalized | mˀ | nˀ | |||||||
| Approximant | plain | l | j | w | |||||
| glottalized | lˀ | ||||||||
- ^1 The plain stops are partially voiced in syllable-initial position.[29]
- ^2 For some speakers, [t͡ʃ] occurs only at the beginning of syllables, while [t͡s] does not occur there, making them allophones of the same phoneme.[30]
- ^3 In Northern Haida (Masset Haida and Alaskan Haida), /χ ɢ̥/ historically developed into /ħ ʕ/, with /χ ɢ̥/ then being reintroduced by occasional borrowings from Southern Haida, Tlingit, Tsimshian, and Chinook jargon.[28][31] The actual realization of the pharyngeal consonants /ħ ʕ/ varies with dialect.[25] In Masset Haida they are pharyngeal fricatives, [ħ, ʕ], whereas in the variety of Alaskan Haida spoken in Hydaburg they have been described as an epiglottal trill [ʜ] and a trilled epiglottal affricate [ʡʢ] or an epiglottal stop [ʡ] respectively.[25][32]
In Alaskan Haida, all velar, uvular, and epiglottal consonants, as well as /n l j/ for some speakers, have rounded variants resulting from coalescence of clusters with /w/.[33] Alaskan Haida also shows simplification of /ŋ/ to /n/ when preceding an alveolar or postalveolar obstruent, and of /sd̥͡ɮ̊/ to /sl/.[34]
In Skidegate Haida, /x/ has allophone [h] in syllable-final position.[27]
Masset Haida phonology is complicated by various spreading processes caused by contiguous sonorants across morpheme boundaries, caused by loss of consonants in morpheme-initial position.[35]
Vowels edit
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The high vowels /i iː u uː/ may be realized as upper mid to high and include lax as well as tense values.[38]
The vowels /ɛː ɔː/ are rare in Skidegate Haida.[38] /ɔː/ only occurs in some interjections and borrowings, and /ɛː/ only occurs in the two words tleehll "five" and tl'lneeng (a clitic).[38] In Masset Haida /ɛ/ and /ɛː/ are both very common are involved in spreading and ablaut processes.[28] Alaskan Haida has neither of these, but has a diphthong /ei/, introduced from contraction of low-toned /əʔi/ and /əji/ sequences.[39]
In Skidegate Haida, some instances of the vowel /a/ are on an underlying level unspecified for quality; Enrico (2003) marks specified /a/ with the symbol ⟨⟩ .[38] Unspecified /a/ becomes /u/ after /w/, /i/ after (non-lateral) alveolar and palatal consonants, and syllabic /l/ after lateral consonants.[38][nb 2] This does not exist in Masset Haida.[28] A small class of Masset Haida words has a new vowel in place of this unspecified vowel which differs in quality from the vowel /a/.[40]
/ə/ is the short counterpart of /aː/ and so can also be analyzed as /a/. Though quite variable in realization, it has an allophone [ʌ] when occurring after uvular and epiglottal consonants.[41] The sequences /jaː/ and /waː/ tend towards [æː] and [ɒː] for some speakers.[42]
A number of the contrasts between vowels, or sequences of vowels and the semivowels /j/ and /w/, are neutralized in certain positions:
- The short vowels do not contrast after the alveolar and postalveolar fricatives and affricates. Only one short vowel occurs in this position, in Alaskan Haida usually realized as [e], but [i] when further followed by /j/, and [u] when followed by any rounded consonant.[41]
- The contrasts of /i/ with /jə/, and /u/ with /wə/ are neutralized when preceded by a velar/uvular/epiglottal consonant, as well as word-initially before the glottal stop.[43]
- No contrast exists between long high vowels and short high vowels followed by a semivowel. Thus, /iː/ is equivalent to /ij/, and /uː/ is equivalent to /uw/;[43] moreover, /wiː/ is also equivalent to /uj/, and /juː/ to /iw/.[44]
- After consonants other than velar/uvular/epiglottal, /əj/ and /əw/ are also neutralized to /iː/ and /uː/.[43]
- Long vowels are shortened before syllable-final glottal consonants, the high vowels /iː uː/ also before sonorant (nasal or approximant) consonants. Where productive, this is a late process that applies after the preceding neutralizations, so that e.g. /qʰwaːʔáːj/ "the rock" is realized as [qʰwʌʔáːj], not [qʰuʔáːj].[45]
The vowels /ɯ ɜ æ/ and short /o/ occur in nonsense syllables in Haida songs.[46]
Tone edit
Haida features phonemic tone, the nature of which differs by dialect.
The Canadian dialects (Skidegate and Masset) have a tone system with low functional load.[40] Unmarked heavy syllables (those with long vowels or ending in sonorants) have high pitch, and unmarked light syllables have low pitch: gid [ɡ̊ìd̥] "dog", gin [ɡ̊ín] "sapwood".[40] Examples of marked syllables include sùu "among" (Masset), k'á "tiny" (Skidegate).[47] In Masset Haida marked low tone syllables are more common, resulting from elision of intervocalic consonants: compare Skidegate 7axad to Masset 7àad "net".[47] Some alternations may be interpreted as results of syllable parsing rather than marked tone: compare Masset q'al.a [qʼálà] 'muskeg' to q'ala [qʼàlà] 'be suspicious of', where . marks a syllable boundary.[47]
In Skidegate Haida, short vowels which do not have marked tone are phonetically lengthened when they are in a word-initial open syllable, thus q'an [qʼán] "grass" becomes q'anaa [qʼàːnáː] "grassy".[16]
In Masset Haida, marked low tone syllables have extra length, thus ginn "thing", 7aww "mother".[48]
In Kaigani, the system is primarily one of pitch accent, with at most one syllable per word featuring high tone in most words, though there are some exceptions (e.g. gúusgáakw "almost"), and it is not always clear what should be considered an independent "word".[46][49] High tone syllables are usually heavy (having a long vowel or ending in a sonorant).[50]
Phonotactics edit
The syllable template in Haida is (C(C(C))V(V)(C(C)).[40] In Skidegate Haida the two unaspirated stops /p t/ can occur in the syllable coda, while none of the other unaspirated or aspirated stops can.[27] In Masset Haida the unaspirated stops and affricates which may be in the syllable coda are /p t t͡s t͡ʃ k/,[28] in Alaskan Haida /p t t͡s t͡ɬ k kʷ ʡ͡ʜ/.[51] Would-be final /q/ in loanwords may be nativized to zero.[52]
In Skidegate Haida a long syllabic lateral may appear in VV position, e.g. tl'll "sew".[28] Historically this developed from long ii after a lateral consonant, but a few Skidegate words retain ii in this position, e.g. qaahlii "inside", liis "mountain goat wool".[28] Syllabic resonants occur frequently in Masset Haida and occasionally in Kaigani Haida, but they are not present on the phonemic level.[37]
First orthography edit
Several orthographies have been devised for writing Haida. The first alphabet was devised by the missionary Charles Harrison[53] of the Church Mission Society who translated some Old Testament Stories in the Haida Language,[54] and some New Testament books. These were published by the British and Foreign Bible Society with the Haida Gospel of Matthew in 1891,[55] Haida Gospel of Luke in 1899[56] and the Haida Gospel of John in 1899,[57] and the book of Acts in Haida in the 1890s.
Modern orthography edit
The linguist John Enrico created another orthography for Skidegate and Masset Haida which introduced ⟨7⟩ and ⟨@⟩ as letters and did away with the distinction between upper and lower case, and this system is popular in Canada.[58][59][60] Another alphabet was devised by Alaska Native Language Center (ANLC) for Kaigani Haida in 1972, based on Tlingit orthographic conventions, and is still in use.[citation needed] Robert Bringhurst, for his publications on Haida literature, created an orthography without punctuation or numerals, and few apostrophes; and in 2008 the Skidegate Haida Immersion Program (SHIP) created another, which is the usual orthography used in Skidegate.[61] Other systems have been used by isolated linguists.[60] Haida consonants are represented as follows.
| Spelling | Phoneme | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrico Masset |
Enrico Skidegate |
ANLC | SHIP | Bringhurst | |
| b | b̥ | ||||
| c | x | x | |||
| d | d̥ | ||||
| dl | d̥͡ɮ̊ | ||||
| g | ɡ̊ | ||||
| G | r | ĝ | g̱ | gh | ɢ̥ |
| h | h | ||||
| hl | ɬ | ||||
| j | d̥͡ʒ̊ | ||||
| k | kʰ | ||||
| kʼ | kk | kʼ | |||
| q | ḵ | q | qʰ | ||
| qʼ | ḵʼ | qʼ | |||
| l | l | ||||
| ʼl | ll | lˀ | |||
| m | m | ||||
| ʼm | mm | mˀ | |||
| n | n | ||||
| ʼn | nn | nˀ | |||
| ng | ŋ | ||||
| p | pʰ | ||||
| pʼ | – | pʼ | |||
| r | g̱ | – | gh (ʻ) | ʕ̥ | |
| s | s | ||||
| t | tʰ | ||||
| tʼ | tt | tʼ | |||
| tl | t͡ɬʰ | ||||
| tlʼ | ttl | t͡ɬʼ | |||
| ts (ch) | t͡s | ||||
| tsʼ | tts | t͡sʼ | |||
| w | w | ||||
| x | x̱ | – | ħ | ||
| X | x | x̂ | x̱ | xh | χ |
| y | j | ||||
| 7 | ʼ | ʔ | |||
| Enrico Masset |
Enrico Skidegate |
ANLC | SHIP | Bringhurst | Phoneme |
In ANLC orthography ⟨ch⟩ is used for ⟨ts⟩ in syllable-initial position, and a hyphen is used to distinguish consonant clusters from digraphs (e.g. kwáan-gang contains the sequence /n/ followed by /ɡ/ rather than the consonant /ŋ/).[59] Bringhurst uses a raised dot for the same, kwáan·gang. The Enrico orthography uses ⟨l⟩ (or ⟨ll⟩ when long) for the syllabic lateral in Skidegate Haida, e.g. tl'l.[46][59] Enrico uses a period ⟨.⟩ for an "unlinked consonant slot."[37] ⟨r x⟩ are used for /q χ/ in Enrico's Skidegate orthography since they generally correspond to /ʡ͡ʜ ʜ/ in the other dialects.[59]
The following are how Haida vowels are written:
| Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| Close | i ii | u uu |
| Mid | e ee | o oo |
| Open | a aa | |
Enrico (2003) uses ⟨@⟩ for some instances of /a/ based on morphophonemics. Alaskan Haida also has a diphthong written ⟨ei⟩. Enrico & Stuart (1996) use ⟨ï ë ä⟩ for the vowels /ɯ ɜ æ/ that occur in nonsense syllables in songs.[46] The Alaskan Haida orthography was updated in 2010 by Jordan Lachler.[63]
Grammar edit
Morphology edit
The word classes in Haida are nouns, verbs, postpositions, demonstratives, quantifiers, adverbs, clitics, exclamations, replies, classifiers, and instrumentals.[64] Unlike in English, adjectives and some words for people are expressed with verbs, e.g. jáada "(to be a) woman", 'láa "(to be) good".[65] Haida morphology is mostly suffixing.[66] Prefixation is only used to form "complex verbs", made up of a nominal classifier or instrumental plus a bound root, for instance Skidegate sq'acid "pick up stick-object" and ts'icid "pick up several (small objects) together, with tongs", which share the root cid "pick up".[67] Infixation occurs with some stative verbs derived from classifiers, for instance the classifier 7id plus the stative suffix -(aa)gaa becomes 7yaadgaa.[67]
The definite article is suffixed -aay.[68] Some speakers shorten this suffix to -ay or -ei.[69] Some nouns, especially verbal nouns ending in long vowels and loan words, take -gaay instead, often accompanied by shortening or eliding preceding aa.[70][nb 3] Haida also has a partitive article -gyaa, referring to "part of something or ... to one or more objects of a given group or category," e.g. tluugyaa uu hal tlaahlaang 'he is making a boat (a member of the category of boats).'[71][nb 4] Partitive nouns are never definite, so the two articles never co-occur.[72]
Personal pronouns occur in independent and clitic forms, which may each be in either agentive or objective form; first and second person pronouns also have separate singular and plural forms.[73] The third person pronoun is only used for animates, though for possession ahljíi (lit. "this one") may be used; after relational nouns and prepositions 'wáa (lit. "it, that place, there") is used instead.[74]
| Indep. | Clitic | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agentive | Objective | Agentive | Objective | ||
| 1 | sg. | hláa | hl | díinaa | díi |
| pl. | tl'áng / t'alang | tl'áng / dalang | íitl'aa | íitl' | |
| 2 | sg. | dáa / dáng | dáng | dáangaa | dáng |
| pl. | dláng / dalang | dláng | dláangaa | dláng / dalang | |
| 3 (anim.) | 'láa | hal | 'láangaa | 'láa / hal 1 | |
| indef. | anim. sg. | - | nang | - | nang |
| anim. pl. | - | tl' | tl'aangaa | tl'aa / tl' 1 | |
| inan. | - | - | - | gin | |
| reflex. | - | - | aangaa | án / -ang 2 | |
| recip. | - | - | gut-áangaa | gut / gu 1 | |
- short form used as bound possessive pronoun before dependent nouns and cliticized to intransitive verbs (that take an objective argument); long form used as bound possessive pronoun before relational nouns and prepositions, and cliticized to transitive verbs
- an is the object pronoun, while -ang is the bound possessive pronoun, suffixed to the noun or preposition it modifies
Number is not marked in most nouns, but is marked in certain cases in verbs.[76] Relationship nouns do have a plural in with -'lang (or for many speakers -lang), e.g. díi chan'láng "my grandfathers".[77][nb 5] A few verbs have suppletive plural forms, as in many other North American languages.[76] In addition, Haida has a plural verb suffix -ru (Skidegate) -7wa (Masset) -'waa / -'uu (Kaigani) that is used to indicate that some third person pronoun in the sentence is plural, and to mark plural subject in imperatives.[76][78] The third person pronoun that is pluralized can have any grammatical function, e.g. tsiin-ee 'laangaa hl dah rujuu-7wa-gan "I bought all their fish" (Masset).[76]
Most nouns referring to family relationships have special vocative forms, e.g. chanáa (Alaskan) chaníi (Masset) "grandfather!"[79]
Haida uses so-called "relational nouns" referring to temporal and spatial relations in place of most prepositions or prepositional phrases in English.[77] Many of these are formed with the suffix -guu, or in Alaskan Haida more often -kw.[80] The updated orthography for Alaska Haida has changed the -kw to -gw. For example, Haida únkw / ínkw / ánkw "surface" likely comes from ún "back (noun)", and Alaskan Haida dítkw "side facing away from the beach, towards the woods" comes from the noun (a)díit "away from the beach, place in the woods".[80] These contrast with "local nouns", which refer to localities and do not occur with possessive pronouns, e.g. (a)sáa "above, up".[81] Some local nouns have an optional prefix a- which does not have semantic value.[81] Both relational and local nouns may take the areal suffix -sii to refer to the entire area rather than a particular location, so for example 'waa ungkw means "[at some place] on its surface" while 'waa ungkwsii means "its surface area".[82]
Haida has a small class of true postpositions, some of which may be suffixed to relational nouns.[83] The Alaskan postpositions -k "to" and -st "from" (Skidegate -ga, -sda) fuse to the preceding word.[83] The Alaskan postposition of -k has been updated in the current Alaska Haida orthography to -g. These also fuse with a preceding suffix -kw to become -gwiik and -guust.[83] The updated orthography for Alaska Haida has changed the -kw to -gw. Some postpositions have forms beginning with ǥ- which are used in some common constructions without a preceding possessive pronoun, and translate into English as a pronoun plus "it", e.g. ǥáa hal gut'anánggang "he's thinking about it" (with ǥáa for aa "to, at").[81]
Haida demonstratives are formed from the bases áa (close to speaker), húu (close to listener), 'wáa (away from both), and a(hl) (something previously mentioned), which when used independently are place demonstratives.[84] These may be given the following suffixes to create other demonstratives: jii (singular object), sgaay (plural objects), s(d)luu (quantity or time), tl'an (place), tl'daas (plural people), tsgwaa (area), and k'un (manner).[84]
Haida verbs have three basic forms: the present, the past, and the inferential forms.[85] The past and inferential forms are both used to refer to events in the past, but differ in evidentiality: the inferential marks that the speaker was informed of or inferred the event rather than having experienced it personally.[86] The bare present form refer to present-tense events, while future is formed with the suffix -saa, using a present-form verb, e.g. hal káasaang "he will go".[87] The interrogative past form, made from the inferential form by removing final n, is used in place of both past and inferential forms in sentences with question words.[88]
There are four classes of verb stems:[nb 6]
| ending in "weak" -aa | ending in "strong" vowel or h | ending in consonant other than t or s | ending in t or s | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| stem | ḵats'áa | st'i | dáang | chat'as |
| present | ḵats'aang | st'igáng | dáanggang | chat'íijang |
| past | ḵats'gán | st'igan | dáanggan | chat'íijan |
| inferential | ḵats'áayaan | st'igaan | dáangaan | chat'ajaan |
| meaning | "go, come inside" | "be sick" | "leave, throw away" | "wear" |
Habitual aspect uses the suffix -gang in the present and inferential and -(g)iinii in the past.[90] Potential mood is marked with -hang and hortative with the particle ts'an (in the same position as the tense suffixes).[91] Imperatives are marked with the particle hl after the first phrase in the sentence, or hlaa after the verb word (the verb dropping final weak aa if present) if there is no non-verbal phrase.[92][nb 7] Verbs are negated with the negative suffix -'ang, usually with the negative word gam "not" in sentence-head position.[93] Verbs drop weak -aa before this suffix, e.g. gám hín hal ist-ánggang "he is not doing it that way".[93]
Haida uses instrumental prefixes, classificatory prefixes, and directional suffixes to derive verbs.[94] Some verb stems, known as bound stems, must occur with at least one such affix; for example -daa "strike once" requires an instrumental prefix.[94]
Haida has a large number of classifiers (on the order of 475).[64] These have a limited number of rhyme structures, which relate to each other ideophonically.[64]
Numerals are generally treated as verbs in Haida, e.g. vdíi git'aláng sdáansaangaangang "I have eight children" (literally "my children are eight").[95] For some types of objects, classificatory prefixes are used, e.g. sdlakw dlasáng "two land otters" (dla- = small animal or fish).[95]
Nouns and verbs that end in a vowel undergo glide formation (if the final vowel is high) or truncation (otherwise) before vowel-initial prefixes.[16] Some vowel-initial suffixes cause nouns and verbs which are consonant-final and polysyllabic to undergo Final Syllable Shortening (FSS).[16]
- sk'u "high water" + -aay 'DF' → sk'waay (Masset)
- st'a "foot" + -aang "own" → st'aang (Skidegate)
- k'ugansaan "bladder" + -ang "own" → k'ugansanang (Masset)
In Masset Haida, final short vowels in polysyllabic verbs are lengthened in sentence-final position: compare Masset dii-ga-hl 7isdaa to Skidegate dii-gi-hla 7isda "Give it to me".[66]
Syntax edit
Haida clauses are verb-final.[96] SOV word order is always possible, while OSV may also be used when the subject is more 'potent' than the object; thus Haida is a direct–inverse language.[97] For example, a human is more potent than a horse, which is more potent than a wagon.[97] Thus the Masset Haida sentence yaank'ii.an-.uu Bill x-aay gu'laa-gang can only mean "truly Bill likes the dog", while yaank'ii.an.uu xaay Bill gu'laa-gang can mean either "truly the dog likes Bill" or "truly Bill likes the dog".[97] The determinants of potency are complex and include "acquaintance, social rank, humanness, animacy.. number ... [and] gender was also important at least in the two southern dialects."[98] The following groups are listed in descending order of potency: "known single adult free humans; non-adult and/or enslaved and/or unknown and/or grouped humans; non-human higher animals; inanimates and lower organisms (fish and lower)."[98] Grammatical definiteness does not affect potency.[99]
Pronouns are placed adjacent to the verb and cliticized to it.[100] Their internal order is object–subject, or in causatives object-causee-subject, for example Bill dii dalang squdang-hal-gan Bill me you punch-direct.that-PA "You told Bill to punch me / Bill told you to punch me".[100][nb 8] Potency is also relevant for pronoun ordering when one pronoun is less potent, for example the indefinite pronoun ga in 'laa ga 7isda-gan = ga 'la 7isda-gan 'she took some.'[101] Sentences with nang "someone" or tl' "some people" as the subject may be translated as passive sentences in English, for example láa tl' ḵínggan "he was seen (by more than one person)", literally "some people saw him".[102]
Clitic pronouns are used as complements of verbs, as inalienable possessives, with quantifiers, and in Skidegate Haida as the objects of some postpositions.[73] Independent pronouns are used everywhere else.[73] Agentive pronouns are marked and are only used as subjects of some verbs.[103] Verbs taking agentive subjects are most common in the lexicon (about 69%), followed by those taking objective subjects (29%) and those that may take either (2%).[104] Intransitive verbs of inherent states (e.g. "be old") take an objective subject, while most transitive verbs take agentive subjects (but cf. verbs like gu'laa "like").[105] With some verbs that may take either, there may be a semantic difference involved, e.g. gwaawa (Masset) which means "refuse" with agentive subject but not want with objective subject.[106] Enrico (2003) argues that the agentive case indicates planning; thus Haida is essentially an active–stative language, though subject case is also variable in some transitive verbs.[106]
Enclitics are placed after the first phrase in the sentence, usually a noun phrase (except with the imperative clitic hl(aa) which follows a verb phrase).[107] Independent pronouns are used instead of clitic pronouns when modified by a clitic, so for example hal ngíishlgan "he got well" becomes l'áa háns ngíishlgan "he also got well" when the clitic háns 'also, too' is added.[107] The enclitics -uu and -kw follow other enclitics.[108]
Focus and less commonly topic are marked with the clitic -.uu~-huu, placed after a sentence-initial constituent, e.g. Bill-.uu Mary qing-gan (Skidegate) "Bill saw Mary" / "Mary saw Bill", 7ahl7aaniis-.uu "qaagaa" hin.uu 'la kya.a-gaa-n "That one, he was called 'qaagaa'".[109][nb 9] Question words always take this enclitic, for example guusuu "what?", tláanuu "where?", gíisanduu "when?".[110]
There are multiple ways that Haida marks possession. Haida has obligatory possession, a common feature of native North American languages where certain nouns (in Haida, family relationship, body part, and "relational" nouns) must occur with a possessor and cannot stand alone.[111] For example, one can say díi aw "my mother" but not *aw, though one may use a circumlocution like nang awáa 'one who is a mother'.[112] These nouns are possessed using the bound objective pronouns, which all precede the noun except -(a)ng 'one's own'.[79][nb 10] Included in the class of obligatorily possessed nouns are so-called "relational nouns" and postpositions, which generally translate to prepositions or prepositional phrases in English and refer to temporal and spatial relations.[113]
Relational nouns take some special third person possessive pronouns ('láa, 'wáa, tl'áa rather than hal, ahljíi, tl'), e.g. 'wáa ḵáahlii "in(side) it" (lit. "its interior").[80] Non-obligatory possession nouns are possessed by putting them in definite form after the possessor (a noun or a bound objective pronoun) in partitive form, e.g. ítl'gyaa yaats'áay "our knife".[114][nb 11] An alternate construction when the possessor is a pronoun is to place an independent objective pronoun after the possessed noun, the latter in definite form, e.g. náay díinaa "my house".[114] The independent objective pronouns also occur by themselves with possessive force, e.g. díinaa "mine".[82]
Examples edit
Phrases in the Alaskan dialect edit
| Kíl 'láa | Hello/ goodbye |
| Sán uu dáng G̱íidang | How do you do? |
| Díi 'láagang | I'm fine |
| Haw'áa | Thank you |
| Dáng díi Ḵuyáadang | I love you |
| Sán uu dáng kya'áang? | What's your name? |
| ... hín díi kya'áang | My name is ... |
| Háws dáng díi Ḵíngsaang | I'll see you again |
| Hingáan an hl gu Ḵuyáat-'uu | Just love one another |
| Gíistgaay gúust uu dáng Ḵ'wáalaagang? | Whose moiety do you belong to? |
Notes edit
- ^ Keen also translated 3 books of the New Testament into Haida: Acts, published in 1898; and the gospels of Luke and John, published 1899. Hatch, Melville H. (Autumn 1957). "A Biographical Memoir of Rev. Keen". The Coleopterists Bulletin. XI (3/4): 62–64. JSTOR 3999009.
- ^ This may occur after FSS, for instance kwasaaw 'pig' + -aay 'DF' becomes kwasiwaay, see Enrico (2003:17).
- ^ In Alaskan Haida, the definite article takes high tone if added to a low-tone syllable, and also takes the high tone from stems ending in a sonorant, nasal, or /iː/ or /uː/ "unless their vowel is lengthened", e.g. x̱akw "halibut" becomes x̱agwáay. See Lawrence (1977:61)
- ^ In Alaskan Haida, -gyaa takes high tone if the noun does not have a high tone already. See Lawrence (1977:65)
- ^ As seen in this example, the suffix takes high tone after a low-tone stem. Also note that the suffix -(a)ng 'one's own' disappears after this suffix. See Lawrence (1977:68)
- ^ The stem of a verb, which is "the form which most people will give as the basic form of a verb if you ask them how to say 'to do so and so'", may be determined by removing -saang from the future form of the verb, e.g. kíngsaang "will see" has stem kíng "to see". See Lawrence (1977:78)
- ^ This clitic hl becomes hahl if the previous word ends in a lateral consonant. See Lawrence (1977:149)
- ^ When both pronouns are object pronouns, the pronoun translating to a subject in English comes last. See Lawrence (1977:147)
- ^ In Masset this is elided after words with final uu, see Enrico (2003:246)
- ^ The suffix -(a)ng behaves like -aay tonally, thus for instance awáng '[someone's] own mother' has high tone on the suffix.
- ^ An exception to this construction is that gyáagan is used for "my" instead of the expected *díigyaan, e.g. gyáagan x̱áay "my dog". See Lawrence (1977:65)
References edit
- ^ Haida at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)
Northern Haida at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)
Southern Haida at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022) - ^ Laurie Bauer, 2007, The Linguistics Student's Handbook, Edinburgh
- ^ Hume, Stephen (17 March 2014). "A high-tech fight to save B.C.'s indigenous languages". The Vancouver Sun.
- ^ a b c d e Enrico (2003:1)
- ^ a b c Enrico (2003:2)
- ^ Enrico (2003:2–3)
- ^ Lyle Campbell (1997) American Indian Languages, p. 24
- ^ Enrico (2003:3)
- ^ a b c Enrico (2003:4)
- ^ Enrico (2003:5)
- ^ a b c d e f Enrico (2003:6)
- ^ Beolens, Bo; et al. (2009). The Eponym Dictionary of Mammals. JHU Press. p. 220. ISBN 9780801895333.
- ^ a b c d Enrico (2003:7)
- ^ Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (3rd ed.). UNESCO. 2010. ISBN 978-92-3-104096-2. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- ^ a b c Lachler, Jordan. "Haida Language Mainpage". Retrieved 23 May 2008.
- ^ a b c d Enrico (2003:17)
- ^ Enrico (2003:8)
- ^ Lisa Phu (Director) (22 October 2013). "UAS and Yukon College partnership advances Native language efforts". KTOO, Juneau, Alaska. 3:44 minutes in. Retrieved 24 October 2013.
{{cite episode}}: Missing or empty|series=(help) - ^ "FirstVoices: Hlg̱aagilda X̱aayda Kil Welcome Page". Retrieved 19 January 2013.
- ^ Porter, Catherine (11 June 2017). "Reviving a Lost Language of Canada Through Film". The New York Times.
- ^ "Canadian film made in language spoken by just 20 people in the world". the Guardian. 28 March 2019.
- ^ a b c Enrico (2004:229)
- ^ Schoonmaker, Von Hagen & Wolf (1997:257)
- ^ "Dene–Yeniseic Symposium". Archived from the original on 26 May 2009. Retrieved 17 March 2008.
- ^ a b c d e Mithun (2001:18)
- ^ Mithun (2001:17)
- ^ a b c Enrico (2003:10)
- ^ a b c d e f g Enrico (2003:12)
- ^ Enrico & Stuart (1996:x–xi)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:18)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:48–49)
- ^ Bessell, Nicola J. "Preliminary Notes on Some Pacific Northwest Coast Pharyngeals" (PDF). University of Pennsylvania. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- ^ Lawrence (1977:27–28)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:45–46)
- ^ Enrico (2003:16)
- ^ Enrico (2003:10–11)
- ^ a b c Enrico & Stuart (1996:xi)
- ^ a b c d e Enrico (2003:11)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:20, 42)
- ^ a b c d Enrico (2003:13)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:32–33)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:26)
- ^ a b c Lawrence (1977:35)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:27)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:36)
- ^ a b c d Enrico & Stuart (1996:xii)
- ^ a b c Enrico (2003:14)
- ^ Enrico (2003:15)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:53–55)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:50–51)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:30)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:49)
- ^ "Queen Charlotte Islands; The Reverend And Mrs. Charles Harrison With Haida Indians - RBCM Archives". search-bcarchives.royalbcmuseum.bc.ca. Retrieved 16 July 2021.
- ^ Old Testament Stories in the Haida Language on archive.org
- ^ Haida Gospel of Matthew on archive.org
- ^ Haida Gospel of Luke on archive.org
- ^ Haida Gospel of John on archive.org
- ^ Enrico & Stuart (1996:x)
- ^ a b c d e Lachler, Jordan. "Ways of Writing Haida". Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- ^ a b c Harvey, Chris (2008). "Haida Language". Retrieved 25 November 2012.
- ^ Bringhurst, Robert (2011). "Appendix 1". A Story as Sharp as a Knife: The Classical Haida Mythtellers and Their World. Douglas & McIntyre. p. 429. ISBN 978-1553658399.
- ^ Enrico & Stuart (1996:xi–xii)
- ^ Lachler, Jordan (22 June 2016). "Dictionary of Alaskan Haida" (PDF). Dictionary of Alaskan Haida. Sealaska Heritage Institute. Retrieved 22 June 2016.
- ^ a b c Enrico (2003:21)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:57–58)
- ^ a b Enrico (2003:19)
- ^ a b Enrico (2003:20)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:59)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:60)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:63)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:64)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:65)
- ^ a b c Enrico (2003:92)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:151)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:150–151)
- ^ a b c d Enrico (2003:24)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:68)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:124, 128)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:67)
- ^ a b c Lawrence (1977:69)
- ^ a b c Lawrence (1977:71)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:72)
- ^ a b c Lawrence (1977:70)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:152)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:78)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:79)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:125)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:125–126)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:79–88)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:123, 125)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:125, 128)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:128)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:123)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:91)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:144)
- ^ Enrico (2003:45)
- ^ a b c Enrico (2003:74–75)
- ^ a b Enrico (2003:76)
- ^ Enrico (2003:109)
- ^ a b Enrico (2003:46)
- ^ Enrico (2003:78)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:148)
- ^ Enrico (2003:92–93)
- ^ Enrico (2003:95)
- ^ Enrico (2003:93–94)
- ^ a b Enrico (2003:96)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:145)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:146)
- ^ Enrico (2003:193, 251–252, 254)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:153)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:66, 68)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:66)
- ^ Lawrence (1977:68, 70)
- ^ a b Lawrence (1977:65–66)
Bibliography edit
- Enrico, John; Stuart, Wendy Bross (1996). Northern Haida Songs. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 0-8032-1816-8.
- Enrico, John (2003). Haida Syntax. University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 0-8032-1822-2.
- Enrico, John (2004). "Toward Proto – Na-Dene". Anthropological Linguistics. 46 (3): 229–302.
- Lawrence, Erma (1977). Haida dictionary. Fairbanks: Alaska Native Language Center.
- Mithun, Marianne (2001). The Languages of Native North America. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 052129875X.
- Schoonmaker, Peter K.; Von Hagen, Bettina; Wolf, Edward C. (1997). The Rain Forests of Home: Profile of a North American Bioregion. Island Press. ISBN 1-55963-480-4.
- Steedman, Scott; Collison, Nika (Jisgang) (2011). That Which Makes Us Haida — the Haida Language. Skidegate: Haida Gwaii Museum Press. ISBN 978-0-920651-32-2.
Other publications edit
- Andersen, Doris (1974). Slave of the Haida. Toronto: Macmillan Co. of Canada. ISBN 9780770516338.
- Bengtson, John D (2008). "Materials for a Comparative Grammar of the Dene–Caucasian (Sino-Caucasian) Languages". Aspects of Comparative Linguistics. 3. Moscow: RSUH Publishers: 45–118.
- Dauenhauer, Nora; Dauenhauer, Richard; Black, Lydia, eds. (2008). Anóoshi lingit aaní ká: Russians in Tlingit America: the battles of Sitka, 1802 and 1804. University of Washington Press.
- Dawson, George M. (1880). "Appendix B: Vocabulary of the Haida Indians of the Queen Charlotte Islands". Report on the Queen Charlotte Islands, 1878. ISBN 9780665148880. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- Dürr, Michael; Renner, Egon (1995). "The History of the Na-Dene Controversy: A Sketch". In Renner, Egon; Dürr, Michael (eds.). Language and Culture in North America: Studies in Honor of Heinz-Jürgen Pinnow. Lincom Studies in Native American Linguistics. Vol. 2. Munich: Lincom Europa. pp. 3–18.
- Enrico, John (1983a). "The Haida Language". In Scudder, G. E.; Gessler, Nicholas (eds.). The Outer Shores. Queen Charlotte City, BC: Queen Charlotte Islands Museum Press. pp. 223–248.
- Enrico, John (1983b). "Tense in the Haida Relative Clause". International Journal of American Linguistics. 52: 91–123. doi:10.1086/466008. S2CID 144085511.
- Enrico, John (1986). "Word Order, Focus and Topic in Haida". International Journal of American Linguistics. 49: 136–166.
- Enrico, John (1991). The Lexical Phonology of Masset Haida. Alaska Native Language Center Research Papers. Vol. 8. Fairbanks: Alaska Native Language Center.
- Enrico, John (1998). "Remarks on Pitch in Skidegate Haida". Gengo Kenkyu. 12: 115–120.
- Enrico, John. 2003. Haida Syntax. (2 volumes). Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press.
- Enrico, John. 2005. Haida Dictionary: Skidegate, Masset, and Alaskan Dialects. (2 volumes). Fairbanks: Alaska Native Language Center; Juneau: Sealaska Heritage Institute.
- Fisher, Robin. 1992. "Contact and Conflict: Indian-European Relations in British Columbia, 1774–1890." UBC Press.
- Greenberg, J.H. 1987a. Language in the Americas. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Greenberg, J.H. 1987b. "The Na-Dene Problem". In Greenberg (1987a), pp. 321–330.
- Harrison, Charles. 1925. "Ancient Warriors of the North Pacific; The Haidas, Their Laws, Customs and Legends." London, H. F. & G. Witherby.
- Harrison, Charles; Royal Society of Canada (1895). Haida grammar (microform). ISBN 9780665063992. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- Hibben & Carswell (1865). Dictionary of Indian tongues (microform) : containing most of the words and terms used in the Tshimpsean, Hydah, & Chinook, with their meaning or equivalent in the English language. ISBN 9780665143663. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- Keen, John Henry (1906). A grammar of the Haida language. Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge. Retrieved 26 August 2012.
- Levine, Robert D. (1979). "Haida and Na-Dene: A New Look at the Evidence". International Journal of American Linguistics. 45 (2): 157–70. doi:10.1086/465587. S2CID 143503584.
- Manaster Ramer, Alexis (1996). "Sapir's Classifications: Haida and the Other Na Dene languages". Anthropological Linguistics. 38: 179–215.
- Pinnow, Heinz-Jürgen (1976). Geschichte der Na-Dene-Forschung. ISBN 3-7861-3027-2.
- Pinnow. H-J. 1985. Das Haida als Na-Dene Sprache. (Abhandlungen der völkerkundlichen Arbeitsgemeinschaft, Hefte 43–46.) Nortorf, Germany: Völkerkundliche Arbeitsgemeinschaft.
- Pinnow. H-J. 2006a. Die Na-Dene-Sprachen im Lichte der Greenberg-Klassifikation. / The Na-Déné Languages in Light of Greenberg's Classification. Zweite erweiterte Auflage / Second revised edition. Bredstedt: Druckerei Lempfert.
- Pinnow. H-J. 2006b. Sprachhistorische Untersuchung zur Stellung des Haida als Na-Dene-Sprache. (Unveränderte Neuausgabe aus INDIANA 10, Gedenkschrift Gerdt Kutscher. Teil 2. Berlin 1985. Mit einem Anhang = Die Na-Dene-Sprachen im Verhältnis zum Tibeto-Chinesischen.) Bredstedt: Druckerei Lempfert.
- Rosman, Abraham; Rubel, Paula G. (1971). Feasting with Mine Enemy: Rank and Exchange among Northwest Coast Societies. Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231034838.
- Ruhlen, M (1998). "The Origin of the Na-Dene". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (23): 13994–13996. Bibcode:1998PNAS...9513994R. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.23.13994. PMC 25007. PMID 9811914.
- Sapir, Edward (1915). "The Na-Dene Languages: A Preliminary Report". American Anthropologist. 17 (3): 534–558. doi:10.1525/aa.1915.17.3.02a00080.
- Stearns, Mary Lee (1981). Haida Culture in Custody. University of Washington Press. ISBN 9780295957630.
- Swanton, John R. 1905. Haida Texts and Myths. Skidegate dialect. (Bureau of American Ethnology Bulletin 29.) Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution.
- Swanton, John R. 1908. Haida Texts. Masset Dialect. (Memoirs of the American Museum of Natural History, vol. 10, part 2.) Leiden: E. J. Brill.
External links edit
- Haida language, archive
- Listen to the sounds of Haida, archive
- Skidegate Haida Portal, First Voices
- Raven, a story in the Haida language
- Haida writing systems, archive
- Haida linguistics bibliography
- The Book of Common Prayer in Haida
- How to count in Haida
- FirstVoices Haida iPhone App
- FirstVoices Haida Online Dictionary
- Haida basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database
- ELAR archive of Northern (Massett) Haida language documentation materials Archived 1 June 2016 at the Wayback Machine
- Dictionary of Alaska Haida
- Alaskan Haida Phrasebook
- Northern Haida (Intercontinental Dictionary Series)


