
Summary
The inferior rectal nerves (inferior anal nerves, inferior hemorrhoidal nerve) usually branch from the pudendal nerve but occasionally arises directly from the sacral plexus; they cross the ischiorectal fossa along with the inferior rectal artery and veins, toward the anal canal and the lower end of the rectum, and is distributed to the sphincter ani externus (external anal sphincter, EAS) and to the integument (skin) around the anus.
| Inferior anal nerves | |
|---|---|
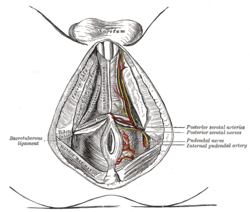 The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery. (Inferior anal nerves visible but not labeled.) | |
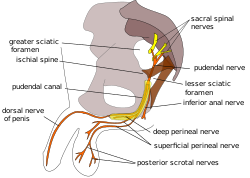 Pudendal nerve, its course through the lesser sciatic foramen, and branches, including inferior anal at bottom right. | |
| Details | |
| From | Pudendal nerve (usually) sacral plexus (occasionally) |
| Innervates | Sphincter ani externus and sensory around the anus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervi anales inferiores, nervi rectales inferiores, nervus haemorrhoidalis inferior |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.038 |
| TA2 | 6555 |
| FMA | 75469 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [edit on Wikidata] | |
Branches of this nerve communicate with the perineal branch of the posterior femoral cutaneous and with the posterior scrotal nerves at the forepart of the perineum.
Supplies edit
Cutaneous innervation below the pectinate line and external anal sphincter.
See also edit
Additional images edit
-
The perineum. The integument and superficial layer of superficial fascia reflected.
-
Sacral plexus of the right side. (Hemorrhoidal branch of pudic labeled at bottom right.)
References edit
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 968 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links edit
- Details Archived 2006-09-01 at the Wayback Machine at Oklahoma State
- Anatomy photo:41:08-0102 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Female Perineum: Contents of the Pudendal Canal"
- Anatomy figure: 41:04-10 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Inferior view of female perineum, branches of the internal pudendal artery."
- perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (analtriangle3)
- figures/chapter_32/32-2.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- figures/chapter_32/32-3.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School


