
Summary
Manganese germanide (MnGe) is an intermetallic compound, a germanide of manganese. Its crystals have a cubic symmetry with no inversion center, they are therefore helical, with right-hand and left-handed chiralities.[1]
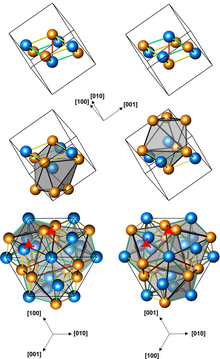 Structures of left-handed and right-handed MnGe crystals (3 presentations, with different numbers of atoms per unit cell; orange atoms are Ge)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Manganese germanide
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| MnGe | |
| Molar mass | 127.57 g/mol |
| 2.17×10−6 emu/g[1] | |
| Structure | |
| Cubic[1] | |
| P213 (No. 198), cP8 | |
a = 0.4795 nm
| |
Formula units (Z)
|
4 |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Manganese silicide |
Other cations
|
Iron germanide Cobalt germanide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Magnetism edit
At low temperatures, MnGe and its relative MnSi exhibit unusual spatial arrangements of electron spin, which were named magnetic skyrmion, tetrahedral and cubic hedgehog lattices. Their structure can be controlled not only by the Si/Ge ratio, but also by temperature and magnetic field. This property has potential application in ultrahigh-density magnetic storage devices.[2]
Synthesis edit
MnGe crystals can be produced by processing a mixture of Mn and Ge powders at a pressure of 4–5 GPa and a temperature of 600–1000 °C for 1–3 hours. They are metastable and decompose into Mn11Ge8 and Ge upon subsequent heating to 600 °C at ambient pressure.[1]
Structure edit
Manganese germanide is a non-stoichiometric compound where the Ge:Mn ratio often deviates from 1. The Mn3Ge5 compound is a Nowotny phase exhibiting a chimney ladder structure. It is either a semimetal or a narrow-gap semiconductor.[3]
References edit
- ^ a b c d Takizawa, H.; Sato, T.; Endo, T.; Shimada, M. (1988). "High-pressure synthesis and electrical and magnetic properties of MnGe and CoGe with the cubic B20 structure". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 73 (1): 40–46. Bibcode:1988JSSCh..73...40T. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(88)90051-5.
- ^ Nagaosa, Naoto; Tokura, Yoshinori (2013). "Topological properties and dynamics of magnetic skyrmions". Nature Nanotechnology. 8 (12): 899–911. Bibcode:2013NatNa...8..899N. doi:10.1038/nnano.2013.243. PMID 24302027.
- ^ Takizawa, H.; Sato, T.; Endo, T.; Shimada, M. (1987). "High-pressure synthesis and electrical properties of Mn3Ge5 with Mn11Si19-type structure". Journal of Solid State Chemistry. 68 (2): 234–238. Bibcode:1987JSSCh..68..234T. doi:10.1016/0022-4596(87)90308-2.


