
KNOWPIA
WELCOME TO KNOWPIA
Summary
Pentazine is a hypothetical chemical compound that consists of a six-membered aromatic ring containing five nitrogen atoms with the molecular formula CHN5. The name pentazine is used in the nomenclature of derivatives of this compound.
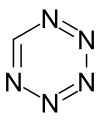
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Pentazine | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| CHN5 | |
| Molar mass | 83.054 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references
| |
Pentazine is predicted to be unstable and to decompose into hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and nitrogen (N2).[1] The activation energy required is predicted to be around 20 kJ/mol.[2]
See also edit
- 6-membered rings with one nitrogen atom: pyridine
- 6-membered rings with two nitrogen atoms: diazines
- 6-membered rings with three nitrogen atoms: triazines
- 6-membered rings with four nitrogen atoms: tetrazines
- 6-membered rings with six nitrogen atoms: hexazine
References edit
- ^ Hurst, Derek T. (1996). "Other Tetrazines and Pentazines". Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry II. pp. 957–965. doi:10.1016/B978-008096518-5.00138-6. ISBN 9780080965185.
- ^ J. Fabian and E. Lewars (2004). "Azabenzenes (azines) — The nitrogen derivatives of benzene with one to six N atoms: Stability, homodesmotic stabilization energy, electron distribution, and magnetic ring current; a computational study" (PDF). Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 82 (1): 50–69. doi:10.1139/v03-178. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2005-03-29.


