
Summary
Provinces are constituent political entities of Zimbabwe. Zimbabwe currently has ten provinces, two of which are cities with provincial status. Zimbabwe is a unitary state, and its provinces exercise only the powers that the central government chooses to delegate. Provinces are divided into districts, which are divided into wards.
| Provinces of Zimbabwe | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Category | Unitary state |
| Location | Republic of Zimbabwe |
| Number | 10 Provinces |
| Populations | 665,952 (Bulawayo) – 2,427,231 (Harare Province) |
| Areas | 1,710 km2 (659 sq mi) (Bulawayo) - 28,967 sq mi (75,025 km2) (Matabeleland North) |
| Government |
|
| Subdivisions | |
The Constitution of Zimbabwe delineates provincial governance and powers. After constitutional amendments in 1988, provinces were administered by a governor directly appointed by the President of Zimbabwe.[1] Since the 2013 constitutional changes, there are technically no longer provincial governors, though in practice they remain in place as Ministers of State for Provincial Affairs. The 2013 Constitution also calls for the devolution of governmental powers and responsibilities where appropriate, though Zimbabwean opposition parties argue that the central government has yet to comply.[2]
With the establishment of Company rule in Rhodesia in the 1890s, the country was divided into two provinces: Matabeleland in the west and Mashonaland in the east. Under British colonial rule as Southern Rhodesia, the colony was divided into five provinces. Later, the Rhodesian government expanded the number of provinces to seven: Manicaland, Matabeleland North and South, Mashonaland North and South, Midlands, and Victoria (today Masvingo).[3] In the 1980s, Mashonaland North and South were reorganized to become three provinces (Mashonaland Central, East and West). The youngest provinces, Bulawayo and Harare, were created in 1997.
| Name | Towns and cities | Established | Population (2022)[4] | Total area[5] | Location | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital | Largest | km2 | mi2 | ||||
| Bulawayo | Bulawayo | 1997 | 665,952 | 900 | 347 | 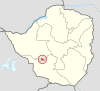
| |
| Harare | Harare | 1997 | 2,427,231 | 872 | 337 | 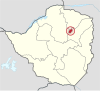
| |
| Manicaland | Mutare | 1897[6] | 2,037,703 | 36,459 | 14,077 | 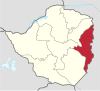
| |
| Mashonaland Central | Bindura | 1983 | 1,384,891 | 28,347 | 10,945 | 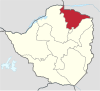
| |
| Mashonaland East | Marondera | ? | 1,731,173 | 32,230 | 12,440 | 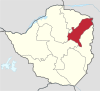
| |
| Mashonaland West | Chinhoyi | Kadoma | 1983 | 1,893,584 | 57,441 | 22,178 | 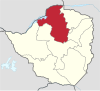
|
| Masvingo | Masvingo | ? | 1,638,528 | 56,566 | 21,840 | 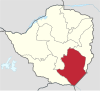
| |
| Matabeleland North | Lupane | Victoria Falls | 1973 | 827,645 | 75,025 | 28,967 | 
|
| Matabeleland South | Gwanda | Beitbridge | 1973 | 760,345 | 54,172 | 20,916 | 
|
| Midlands | Gweru | ? | 1,811,905 | 49,166 | 18,983 | 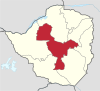
| |
See also edit
External links edit
- Map of Provinces of Zimbabwe - Statoids.org
References edit
- ^ Bridger, Peter Anthony (1973). Encyclopaedia Rhodesia. College Press.
- ^ Kandemiiri, Jonga (1 March 2016). "MDC-T Urges Zimbabwe to Devolve Power to Provinces". VOA. Retrieved 25 July 2018.
- ^ Passmore, Gloria C. (1972). The National Policy of Community Development in Rhodesia. Department of Political Science, University of Rhodesia. p. 163.
- ^ "Zimbabwe: Provinces, Major Cities & Urban Localities - Population Statistics, Maps, Charts, Weather and Web Information". www.citypopulation.de. Retrieved 28 January 2024.
- ^ Zimbabwe at GeoHive
- ^ "Reports of International Arbitral Awards, Volume XXVIII" (PDF). United Nations.
5.Zimbabwe census2012 https://www.citypopulation.de/Zimbabwe-Cities.html


