
Summary
The Santa Fe Island tortoise (Chelonoidis niger ssp.), also known as the Santa Fe tortoise or Santa Fe giant tortoise, is an undescribed extinct taxon of Galápagos tortoise endemic to Santa Fe Island in the Galápagos archipelago in the equatorial eastern Pacific Ocean. Evidence for the historic existence of the tortoise comes from 19th century anecdotes of whalers and settlers removing tortoises from the island, as well as the discovery of tortoise bones there by the 1905–1906 California Academy of Sciences expedition, with genetic examination of the bones indicating that they belonged to a unique taxon most closely related to Chelonoidis niger hoodensis, the Hood Island giant tortoise from Española Island (formerly known as Hood Island).[1]
| Santa Fe Island tortoise | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Testudines |
| Suborder: | Cryptodira |
| Superfamily: | Testudinoidea |
| Family: | Testudinidae |
| Genus: | Chelonoidis |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | †C. n. ssp.
|
| Trinomial name | |
| †Chelonoidis niger ssp. | |
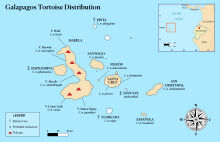
| |
| Map of the Galápagos Islands showing locations of different tortoise species. | |
Ecological restoration edit
Following a decision made at an international workshop on giant tortoises in 2012, a program was initiated to reestablish a tortoise population on Santa Fe, after more than 150 years without one, using the Hood Island subspecies as an ecological analogue, or substitute for the Santa Fe subspecies.[1] Between 2015 and 2021 the Santa Fe Tortoise Project successfully introduced some 700 juvenile and 31 subadult Hood Island tortoises to Santa Fe to complete the third phase of the ecological restoration program for the island.[2]
References edit


