
Summary
Shahrazad is a large crater on Saturn's moon Enceladus first discovered by the Voyager 2 spacecraft. It is located at 47.3° North Latitude, 199.7° West Longitude and is approximately 20 kilometers across.[1] Shahrazad is the middle crater of a prominent crater triplet on Enceladus' anti-Saturnian hemisphere[2] (there is no evidence that the impacts are related or were formed from break-up of a single body, like Shoemaker-Levy 9). Voyager images revealed very little about this crater, however, higher resolution views of Shahrazad taken by the Cassini Spacecraft during a close flyby on March 9, 2005, reveal significant north–south fracturing that runs through all three craters of the triplet. Deep canyons mark the northern and eastern portions of Shahrazad's rim. Some evidence for viscous relaxation can be seen, but it is not nearly as significant as at Dunyazad to its immediate south or at Aladdin elsewhere on the satellite.
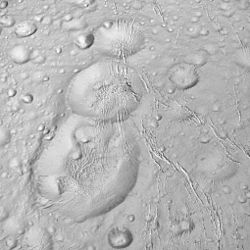 Shahrazad crater (center) as seen by the Cassini spacecraft on October 14, 2015 | |
| Location | 47°18′N 199°44′W / 47.3°N 199.73°W[1] |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 20 km[1] |
| Discoverer | Voyager 2 |
| Naming | Scheherazade; storyteller of One Thousand and One Nights |
Shahrazad is named after the Persian story-teller Scheherazade from One Thousand and One Nights, the Heroine who told 1001 tales over as many nights to Shahryar in order to secure her freedom.
References edit


