
Summary
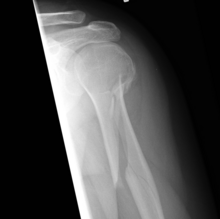
A spiral fracture (a.k.a. torsion fracture) is a bone fracture occurring when torque (a rotating force) is applied along the axis of a bone.[1] Spiral fractures often occur when the body is in motion while one extremity is planted. For example, a spiral fracture of the tibia (the shinbone) can occur in young children when they fall short on an extended leg while jumping. This occurrence is known as "toddler's fracture". Spiral fractures are also recognized as being suspicious in very young children since to obtain a fracture of this sort requires forceful twisting or jerking of the limbs. Child abuse (physical abuse) and certain conditions such as osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) are considered differentials when identifying spiral or torsion fractures.[2]
References edit
- ^ "Spiral Fracture". Harvard University. Archived from the original on 8 August 2010. Retrieved 25 November 2010.
- ^ Lukefahr M.D., James. "Child Abuse and Neglect Fractures". www.utmb.edu. University of Texas Health Science Center. Archived from the original on 26 August 2016. Retrieved 15 December 2014.
External links edit
- http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/osteogenesis-imperfecta


