
KNOWPIA
WELCOME TO KNOWPIA
Summary
Sulfur oxoacids are chemical compounds that contain sulfur, oxygen, and hydrogen. The best known and most important industrially used is sulfuric acid. Sulfur has several oxoacids; however, some of these are known only from their salts (these are shown in italics in the table below). The acids that have been characterised contain a variety of structural features, for example:
- tetrahedral sulfur when coordinated to oxygen
- terminal and bridging oxygen atoms
- terminal peroxo groups
- terminal S=S
- chains of (−S−)n
| Acid | Formula | Formal oxidation number | Structure | Related anions | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 | +6 | 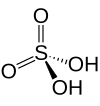
|
Sulfate, SO2− 4 and hydrogen sulfate commonly known as bisulfate, HSO− 4 |
Best known and industrially significant. |
| Polysulfuric acids including disulfuric acid (pyrosulfuric acid) | H2SO4·nSO3 | +6 | 
|
Disulfate (commonly known as pyrosulfate), S 2O2− 7 and trisulfate, S 3O2− 10 |
Pure disulfuric acid melts at 36 °C. Present in fuming sulfuric acid, oleum. Examples known for n = 1 and n = 2. |
| Peroxymonosulfuric acid | H2SO5 | +6 | 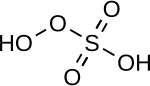
|
Peroxomonosulfate, OOSO2− 3 |
"Caro's acid", a solid melting at 45 °C |
| Peroxydisulfuric acid | H2S2O8 | +6 | 
|
Peroxydisulfate, O 3SOOSO2− 3 |
"Marshall's acid", a solid melting at 65 °C. |
| Dithionic acid | H2S2O6 | +5 | 
|
Dithionate, O 3SSO2− 3 |
Not isolated in pure form, only concentrated solutions have been prepared |
| Thiosulfuric acid | H2S2O3 | 0 (for the terminal sulfur), +4 (for the central atom) | 
|
Thiosulfate, S 2O2− 3 Hydrogenthiosulfate HS 2O− 3 (ammonium salt prepared in anhydrous methanol at −80 °C[1]) |
Aqueous solutions decompose. |
| Disulfurous acid or pyrosulfurous acid | H2S2O5 | +5 (of the sulfur atom bonded to 3 oxygen atoms), +3 (of other sulfur atom) | 
|
Disulfite commonly known as metabisulfite, S 2O2− 5 |
Not known. |
| Sulfurous acid | H2SO3 | +4 | 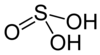
|
Bisulfite, HSO− 3 and sulfite, SO2− 3 |
Not known. |
| Dithionous acid | H2S2O4 | +3 | 
|
Dithionite, O 2SSO2− 2 |
Not known. |
| Sulfoxylic acid | H2SO2 | +2 | Sulfoxylate, SO2− 2 |
Free acid not known | |
| Polythionic acid | H2SxO6 | 0 (for the bridging S atoms), +5 (for the terminal central S atoms) | 
|
Polythionates, O 3S(S x−2)SO2− 3. Example trithionate, tetrathionate, pentathionate, hexathionate, heptathionate, octathionate, nonathionate, decathionate, undecathionate, dodecathionate, tridecathionate, and tetradecathionate. |
Examples known with x = 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10, 12, 14. |
| Thiosulfurous acid | H2S2O2 | −1 (for the exterior sulfur atom ), +3 (for the central atom) | Thiosulfites | Not known | |
| Dihydroxydisulfane | H2S2O2 | +1 | Acid known |
See also edit
References edit
- ^ Raman spectroscopic discovery of the hydrogenthiosulphate anion, HSSO−
3, in solid NH4HS2O3 Steudel Rr.; Prenzel A Zeitschrift für Naturforschung 1989,44, 12, 1499-1502
External links edit
- Sulfur+Acids at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) Sulfur oxoacids along with other acids containing sulfur


