
Summary
A tree view is a graphical widget (graphical control element) within a graphical user interface (GUI) in which users can navigate and interact intuitively with concise, hierarchical data presented as nodes in a tree-like format.[1][2] It can also be called an outline view.
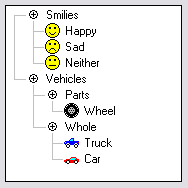
Appearance edit
A tree view is usually a vertical list of nodes arranged in a tree-like structure.[1][2] Each node represents a single data item, displayed as an indented line of text or a rectangular box. The indentation (and sometimes a line drawn between nodes) is used to indicate levels of hierarchy. Every treeview has a root node from which all nodes descend. Below the root node and indented to the right are its child nodes. Each node has exactly one parent node and can have zero or more child nodes. If a node (other than the root node) has a child or children, it is called a branch node. If it has no child, then it is a leaf node.[3] This creates a hierarchical tree-like structure, with branches and subbranches emerging downward and rightwards. The nodes can be differentiated by different colors, icons and fonts to represent the nested relationship between parent nodes and child nodes.[2] An item can be expanded to reveal subitems, if any exist, and collapsed to hide subitems.
Features edit
Interactivity edit
Tree view allows users to interact with hierarchical data in a variety of ways, such as :
- expanding and collapsing nodes to reveal or to hide their child nodes and thus navigate through the tree structure according to one's needs.
- search and filter nodes based on specific criteria such as date.
- renaming or deleting using context menus.
- copying and moving (dragging and dropping) nodes to other sections of the tree to rearrange them.
- opening a node in a separate window.
Customizability edit
Tree views can be customized for visual appeal and efficiency in the following ways:
- Input methods : Tree views can be customized to support various input methods such as mouse, keyboard, and touch input so that users can interact using their preferred method. Users can use their mouse to click on a node to select it, move their mouse to drag and then release the mouse button to drop nodes to rearrange them. They can also use keyboard shortcuts to navigate and interact with the tree.
- Look and feel : Developers (and sometimes users) can tailor the look and feel of tree views as well to match specific visual requirements of certain applications. Icons, fonts and colors used to display nodes, animations and effects to represent node expansion and collapse, and custom behaviors for drag and drop actions can be implemented. The context menu options can be customized for an application so that users can only perform specific actions on nodes.
- Accessibility : tree views can offer accessibility features for users with disabilities.
Advantages edit
Tree views offer the following advantages :
- They display hierarchical data in a concise and easy-to-follow format, so that users can easily walk through and interact with the data.
- They are customizable, so their appearance and behavior can be tailored to meet specific requirements of an application.
- They are interactive and allow the use of different input methods.
- They are flexible and potent navigational tools which can be used in a variety of applications (such as file managers)
Disadvantages edit
- If the nested or hierarchical relationship of items is not to be emphasized, then tree view would not be the optimal choice. A regular list would be more appropriate.
- For large amounts of data or deeply nested hierarchies, tree views can become visually disorderly and difficult to navigate, leading to inefficiency and productivity loss because users would spend more time walking through the structure than working with the data.
- They are more complex and thus more difficult to maintain than simpler structures like lists and tables.
- For the developers, customization options with animations and complex behaviors can increase time spent on implementation and debugging.
Application edit
Tree views are used in situations where hierarchical data needs to be displayed and navigated in a graphical interface. For example, they have been used in:
- file managers to display the hierarchical structure of directories and files residing in a computer file system so that users can navigate the directory tree and open, close and manage their files more efficiently.
- email clients to display the hierarchical structure of email folders and messages, helping users to view and reply to email messages, and manage their inbox.
- organizational charts to display the hierarchical structure of an organization's employees and departments.
- network topologies
- programming frameworks for building graphical applications.
- XML documents to present hierarchical data.
- outliner applications (as extended tree view), where each node consists of editable text.
See also edit
- Directory (file systems) - an example of application of tree views
- File manager
- Genealogy software
References edit
- ^ a b Alan D. Moore (2021), Python GUI Programming with Tkinter: Design and build functional and user-friendly GUI applications, Packt Publishing Ltd, p. 238
- ^ a b c "Tree view". Microsoft Learn. 16 March 2023. Retrieved 19 April 2023.
- ^ "How to Use Trees". The Java™ Tutorials. Retrieved 19 April 2023.
External links edit
- Treeview in pure HTML+CSS
- Tree view widget in the GTK+ API
- Tree view control in the Win32 API (MSDN)
- Yahoo! UI Library y
- Extended TreeView for .NET WinForms
- TreeView Control in ASP.NET 2.0
- Interview with Henk Hagedoorn, developer of first tree-view PIM


