
Summary
A homophone (/ˈhɒməfoʊn, ˈhoʊmə-/) is a word that is pronounced the same (to a varying extent) as another word but differs in meaning. The two words may be spelled the same, for example rose (flower) and rose (past tense of "rise"), or spelled differently, as in rain, reign, and rein. The term homophone sometimes applies to units longer or shorter than words, for example a phrase, letter, or groups of letters which are pronounced the same as a counterpart. Any unit with this property is said to be homophonous (/həˈmɒfənəs/).
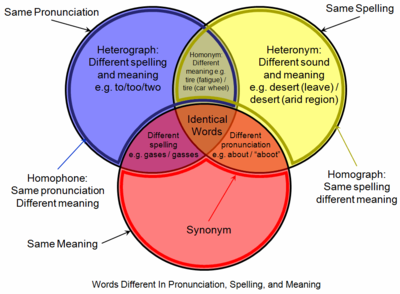
Homophones that are spelled the same are deemed both homographs and homonyms, e.g. the word read, as in "He is well read" (he is very learned) vs. the sentence "I read that book" (I have finished reading that book).[a]
Homophones that are spelled differently are also called heterographs, e.g. to, too, and two.
Etymology edit
"Homophone" derives from Greek homo- (ὁμο‑), "same", and phōnḗ (φωνή), "voice, utterance".
Wordplay and games edit
Homophones are often used to create puns and to deceive the reader (as in crossword puzzles) or to suggest multiple meanings. The last usage is common in poetry and creative literature. An example of this is seen in Dylan Thomas's radio play Under Milk Wood: "The shops in mourning" where mourning can be heard as mourning or morning. Another vivid example is Thomas Hood's use of birth and berth as well as told and toll'd (tolled) in his poem "Faithless Sally Brown":
- His death, which happen'd in his berth,
- At forty-odd befell:
- They went and told the sexton, and
- The sexton toll'd the bell.
In some accents, various sounds have merged in that they are no longer distinctive, and thus words that differ only by those sounds in an accent that maintains the distinction (a minimal pair) are homophonous in the accent with the merger. Some examples from English are:
- pin and pen in many southern American accents
- by and buy
- merry, marry, and Mary in most American accents
- The pairs do and due as well as forward and foreword are homophonous in most American accents but not in most English accents
- The pairs talk and torque as well as court and caught are distinguished in rhotic accents, such as Scottish English, and most dialects of American English, but are homophones in some non-rhotic accents, such as British Received Pronunciation
Wordplay is particularly common in English because the multiplicity of linguistic influences offers considerable complication in spelling and meaning and pronunciation compared with other languages.
Malapropisms, which often create a similar comic effect, are usually near-homophones. See also Eggcorn.
Same-sounding phrases edit
Same-sounding (homophonous, or homophonic) phrases are often used in various word games. Examples of same-sounding phrases (which may only be true homophones in certain dialects of English) include:
- ice cream vs. I scream (as in the phrase I scream. You scream. We all scream for ice cream.)
- euthanasia vs. Youth in Asia
- depend vs. deep end
- Gemini vs. gem in eye vs. Jem and I
- the sky vs. this guy (most notably as a mondegreen in "Purple Haze" by Jimi Hendrix)
- Four Candles vs. fork handles
- real eyes vs. realize vs. real lies (as in the phrase Real eyes realize real lies.)
- philanderers vs. Flanders
- example vs. egg sample
- some others vs. some mothers vs. smothers
American comedian Jeff Foxworthy frequently uses same-sounding phrases in his Appalachian comedy routine, which play on exaggerated "country" accents. Notable examples include:
- Initiate vs. and then she ate: "My wife ate two sandwiches, initiate a bag o' tater chips."
- Mayonnaise vs. Man, there is: "Mayonnaise a lot of people here tonight."
- Innuendo vs. in your window: "Hey dude I saw a bird fly innuendo."
- Moustache vs. must ask: "I Moustache you a question."
During the 1980s, an attempt was made to promote a distinctive term for same-sounding multiple words or phrases, by referring to them as "oronyms",[b] but the term oronym was already well established in linguistics as an onomastic designation for a class of toponymic features (names of mountains, hills, etc.),[2] the alternative use of the same term was not well accepted in scholarly literature.[3]
In various languages edit
English edit
There are sources[4] which maintain lists of homophones (words with identical pronunciations but different spellings) and even 'multinyms.' There is disagreement among such lists due to dialectical variations in pronunciation and archaic uses. In English, concerning groups of homophones (excluding proper nouns), there are approximately 88 triplets, 24 quadruplets, 2 quintuplets, 1 sextet, 1 septet, and 1 questionable octet (possibly a second septet). The questionable octet is:
- raise, rays, rase, raze, rehs, res, reais, [race]
Other than the common words raise, rays, and race this octet includes
- raze – a verb meaning "to demolish, level to the ground" or "to scrape as if with a razor"
- rase – an archaic verb meaning "to erase"
- rehs – the plural of reh, a mixture of sodium salts found as an efflorescence in India
- res – the plural of re, a name for one step of the musical scale; obsolete legal term for "the matter" or "incident"
- reais – the plural of real, the currency unit of Brazil
The inclusion of "race" in the octet above is questionable, since its pronunciation differs from the other words on the list (ending with /s/ instead of /z/).
If proper names are included, then a possible nonet would be:
- Ayr – a town in Scotland
- Aire – a river in Yorkshire
- Eyre – legal term and various geographic locations
- heir – one who inherits
- air – the ubiquitous atmospheric gas that people breathe; a type of musical tune
- err – to make an error
- ere – poetic / archaic "before"
- e'er – poetic "ever" (some speakers)
- are – a defunct, small, metric unit of area
Brazilian Portuguese edit
The Portuguese language has one of the highest numbers of homophones and consequently homographs in the world. Homophonic words include: "Jogo" - I throw, "Jogo" - I play, "Jogo" - Match (Sports), and "Jogo" - Game (This last one is controversial, with dialects like Paulistano considering it non-homophonic, while dialects like Caipira consider it only homophonic, noting that these are two Brazilian dialects.)
For example, "Cinto" is a homophone for 9 other words, totalizing 10.(Oxford Languages)
! Although they are homophones, most of them are also homographs !
- Cinto - a strip of varying width made of fabric, leather, or other material, worn around the waist and tied with a bow or fastened with a buckle or other closure.
- Cinto - any strap or band that encircles the waist or trunk for safety purposes.
- Cinto - synonymous with "CÓS" (waistband).
- Cinto - that which surrounds and/or limits a space; fence.
- Cinto - a ring that encircles something; belt.
- Cinto - "A metal cinto reinforces the columns."
- Cinto - synonymous with "ANILHA" (ring).
- Cinto - a long, narrow bag that travelers attach to the waist or carry over the shoulder.
- Sinto - to touch and feel the texture.
- Sinto - to become sensitive to something
German edit
There are many homophones in present-day standard German. As in other languages, however, there exists regional and/or individual variation in certain groups of words or in single words, so that the number of homophones varies accordingly. Regional variation is especially common in words that exhibit the long vowels ä and e. According to the well-known dictionary Duden, these vowels should be distinguished as /ɛ:/ and /e:/, but this is not always the case, so that words like Ähre (ear of corn) and Ehre (honor) may or may not be homophones. Individual variation is shown by a pair like Gäste (guests) – Geste (gesture), the latter of which varies between /ˈɡe:stə/ and /ˈɡɛstə/ and by a pair like Stiel (handle, stalk) – Stil (style), the latter of which varies between /ʃtiːl/ and /stiːl/.
Besides websites that offer extensive lists of German homophones,[5] there are others which provide numerous sentences with various types of homophones.[6] In the German language homophones occur in more than 200 instances. Of these, a few are triples like
- Waagen (weighing scales) – Wagen (cart) – wagen (to dare)
- Waise (orphan) – Weise (way, manner) – weise (wise)
Most are couples like lehren (to teach) – leeren (to empty).
Spanish edit
Although Spanish has far fewer homophones than English, they are far from being non-existent. Some are homonyms, such as basta, which can either mean 'enough' or 'coarse', and some exist because of homophonous letters. For example, the letters b and v are pronounced exactly alike, so the words basta (coarse) and vasta (vast) are pronounced identically.[7]
Other homonyms are spelled the same, but mean different things in different genders. For example, the masculine noun el capital means 'capital' as in 'money', but the feminine noun la capital means 'capital city'.[8]
Japanese edit
There are many homophones in Japanese, due to the use of Sino-Japanese vocabulary, where borrowed words and morphemes from Chinese are widely used in Japanese, but many sound differences, such as the original words' tones, are lost.[citation needed] These are to some extent disambiguated via Japanese pitch accent (i.e. 日本 vs. 二本, both pronounced nihon, but with different pitches), or from context, but many of these words are primarily or almost exclusively used in writing, where they are easily distinguished as they are written with different kanji; others are used for puns, which are frequent in Japanese.
An extreme example is kikō (hiragana: きこう), which is the pronunciation of at least 22 words (some quite rare or specialized, others common; all these examples are two-character compounds), including:
- 機構 (organization / mechanism)
- 紀行 (travelogue)
- 稀覯 (rare)
- 騎行 (horseback riding)
- 貴校 (school (respectful))
- 奇功 (outstanding achievement)
- 貴公 (word for "you" used by men addressing male equals or inferiors)
- 起稿 (draft)
- 奇行 (eccentricity)
- 機巧 (contrivance)
- 寄港 (stopping at port)
- 帰校 (returning to school)
- 気功 (breathing exercise, qigong)
- 寄稿 (contribute an article / a written piece)
- 機甲 (armor, e.g. of a tank)
- 帰航 (homeward voyage)
- 奇効 (remarkable effect)
- 季候 (season / climate)
- 気孔 (stoma)
- 起工 (setting to work)
- 気候 (climate)
- 帰港 (returning to port)
Even some native Japanese words are homophones. For example, kami (かみ) is the pronunciation of the words
- 紙 (paper)
- 髪 (hair)
- 神 (god / spirit)
- 上 (up)
The former two words are disambiguated from the latter two by pitch accent.
Korean edit
The Korean language contains a combination of words that strictly belong to Korean and words that are loanwords from Chinese. Due to Chinese being pronounced with varying tones and Korean's removal of those tones, and because the modern Korean writing system, Hangeul, has a more finite number of phonemes than, for example, Latin-derived alphabets such as that of English, there are many homonyms with both the same spelling and pronunciation. For example
- '화장(化粧)하다': 'to put on makeup' vs. '화장(火葬)하다': 'to cremate'
- '유산(遺産)': 'inheritance' vs. '유산(流産)': 'miscarriage'
- '방구': 'fart' vs. '방구(防具)': 'guard'
- '밤[밤ː]': 'chestnut' vs. '밤': 'night'
There are heterographs, but far fewer, contrary to the tendency in English. For example,
- '학문(學問)': 'learning' vs. '항문(肛門)': 'anus'.
Using hanja (한자; 漢字), which are Chinese characters, such words are written differently.
As in other languages, Korean homonyms can be used to make puns. The context in which the word is used indicates which meaning is intended by the speaker or writer.
Mandarin Chinese edit
Due to phonological constraints in Mandarin syllables (as Mandarin only allows for an initial consonant, a vowel, and a nasal or retroflex consonant in respective order), there are only a little over 400 possible unique syllables that can be produced,[9] compared to over 15,831 in the English language.[10]
Chinese has an entire genre of poems taking advantage of the large amount of homophones called one-syllable articles, or poems where every single word in the poem is pronounced as the same syllable if tones are disregarded. An example is the Lion-Eating Poet in the Stone Den.
Like all Chinese languages, Mandarin uses phonemic tones to distinguish homophonic syllables; Mandarin has five tones. A famous example,
- mā (妈) means "mother"
- má (麻) means "hemp"
- mă (马) means "horse"
- mà (骂) means "scold"
- ma (吗) is a yes / no question particle
Although all these words consist of the same string of consonants and vowels, the only way to distinguish each of these words audibly is by listening to which tone the word has, and as shown above, saying a consonant-vowel string using a different tone can produce an entirely different word altogether. If tones are included, the number of unique syllables in Mandarin increases to at least 1,522.[11]
However, even with tones, Mandarin retains a very large amount of homophones. Yì, for example, has at least 125 homophones,[12] and it is the pronunciation used for Chinese characters such as 义, 意, 易, 亿, 议, 一, and 已.
There are even place names in China that have identical pronunciations, aside for the difference in tone. For example, there are two neighboring provinces with nearly identical names, Shanxi (山西) and Shaanxi (陕西) Province. The only difference in pronunciation between the two names are the tone in the first syllable (Shanxi is pronounced Shānxī whereas Shaanxi is pronounced Shǎnxī). As most languages exclude the tone diacritics when transcribing Chinese place names into their own languages, the only way to visually distinguish the two names is to write Shaanxi in Gwoyeu Romatzyh romanization. Otherwise, nearly all other spellings of placenames in mainland China are spelled using Hanyu Pinyin romanization.
Many scholars believe that the Chinese language did not always have such a large number of homophones and that the phonological structure of Chinese syllables was once more complex, which allowed for a larger amount of possible syllables so that words sounded more distinct from each other.
Scholars also believe that Old Chinese had no phonemic tones, but tones emerged in Middle Chinese to replace sounds that were lost from Old Chinese. Since words in Old Chinese sounded more distinct from each other at this time, it explains why many words in Classical Chinese consisted of only one syllable. For example, the Standard Mandarin word 狮子(shīzi, meaning "lion") was simply 狮 (shī) in Classical Chinese, and the Standard Mandarin word 教育 (jiàoyù, "education") was simply 教 (jiào) in Classical Chinese.
Since many Chinese words became homophonic over the centuries, it became difficult to distinguish words when listening to documents written in Classical Chinese being read aloud. One-syllable articles like those mentioned above are evidence for this. For this reason, many one-syllable words from Classical Chinese became two-syllable words, like the words mentioned in the previous paragraph.
Even with the existence of two- or two-syllable words, however, there are even multisyllabic homophones. Such homophones even play a major role in daily life throughout China, including Spring Festival traditions, which gifts to give (and not give), political criticism, texting, and many other aspects of people's lives.[13]
Another complication that arises within the Chinese language is that in non-rap songs, tones are disregarded in favor of maintaining melody in the song.[14] While in most cases, the lack of phonemic tones in music does not cause confusion among native speakers, there are instances where puns may arise.
Subtitles in Chinese characters are usually displayed on music videos and in songs sung on movies and TV shows to disambiguate the song's lyrics.
Vietnamese edit
It is estimated that there are approximately 4,500 to 4,800 possible syllables in Vietnamese, depending on the dialect.[15] The exact number is difficult to calculate because there are significant differences in pronunciation among the dialects. For example, the graphemes and digraphs "d", "gi", and "r" are all pronounced /z/ in the Hanoi dialect, so the words dao (knife), giao (delivery), and rao (advertise) are all pronounced /zaw˧/. In Saigon dialect, however, the graphemes and digraphs "d", "gi", and "v" are all pronounced /j/, so the words dao (knife), giao (delivery), and vao (enter) are all pronounced /jaw˧/.
Pairs of words that are homophones in one dialect may not be homophones in the other. For example, the words sắc (sharp) and xắc (dice) are both pronounced /săk˧˥/ in Hanoi dialect, but pronounced /ʂăk˧˥/ and /săk˧˥/ in Saigon dialect respectively.
Psychological research edit
Pseudo-homophones edit
Pseudo-homophones are pseudowords that are phonetically identical to a word. For example, groan/grone and crane/crain are pseudo-homophone pairs, whereas plane/plain is a homophone pair since both letter strings are recognised words. Both types of pairs are used in lexical decision tasks to investigate word recognition.[16]
Use as ambiguous information edit
Homophones, specifically heterographs, where one spelling is of a threatening nature and one is not (e.g. slay/sleigh, war/wore) have been used in studies of anxiety as a test of cognitive models that those with high anxiety tend to interpret ambiguous information in a threatening manner.[17]
See also edit
- "Do-Re-Mi", a show tune from The Sound of Music that uses homophones (e.g. "doe", "ray", "me") to explain the notes in the solfège scale
- Homograph
- Homonym
- Synonym
- Dajare, a type of wordplay involving similar-sounding phrases
- Perfect rhyme
- Wiktionary
- List of dialect-independent homophones
- List of dialect-dependent homophones
Footnotes edit
- ^ According to the strict sense of homonyms as words with the same spelling and pronunciation; however, homonyms according to the loose sense common in nontechnical contexts are words with the same spelling or pronunciation, in which case all homophones are also homonyms.[1]
- ^ The name oronym was first proposed and advocated by Gyles Brandreth in his book The Joy of Lex (1980), and such use was also accepted in the BBC programme Never Mind the Full Stops, which featured Brandreth as a guest.
References edit
- ^ "Homonym". Random House Unabridged Dictionary. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016 – via Dictionary.com.
- ^ Room 1996, p. 75.
- ^ Stewart 2015, p. 91, 237.
- ^ Burkardt, J. "Multinyms". Department of Scientific Computing. Fun / wordplay. Florida State University. Archived from the original on 25 August 2016.
- ^ See, e.g. "Homophone und homonyme im deutschen Homophone". yumpu.com (in German). Archived from the original on 8 March 2021. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ See Fausto Cercignani, "Beispielsätze mit deutschen Homophonen" [Example sentences with German homophones] (in German). Archived from the original on 29 May 2020.
- ^ "51 Spanish Words That Sound Exactly Like Other Spanish Words". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 27 August 2022.
- ^ "37 Spanish Nouns Whose Meanings Change With Gender". ThoughtCo. Retrieved 27 August 2022.
- ^ "Is there any similarity between Chinese and English?". Learn Mandarin Chinese Online. Study Online Mandarin Chinese Courses. 7 July 2017. Archived from the original on 25 January 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2020.
- ^ Barker (22 August 2016). "Syllables". Linguistics. New York University. Archived from the original on 22 August 2016. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- ^ "Compare that with 413 syllables for Chinese if you ignore tones, 1,522 syllables". news.ycombinator.com. Hacker News. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2020.
- ^ Chang, Chao-Huang. "Corpus-based adaptation mechanisms for Chinese Homophone disambiguation" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2020.
- ^ "Chinese Homophones and Chinese Customs". yoyochinese.com (blog). Archived from the original on 9 April 2021. Retrieved 18 December 2020.
- ^ "How do people sing in a tonal language?". Diplomatic Language Services. 8 September 2016. Archived from the original on 28 November 2020. Retrieved 30 December 2020.
- ^ "vietnamese tone marks pronunciation". pronunciator.com. Archived from the original on 18 May 2022. Retrieved 5 February 2021.
- ^ Martin, R.C. (1982). "The pseudohomophone effect: The role of visual similarity in non-word decisions". Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology. 34A (Pt 3): 395–409. doi:10.1080/14640748208400851. PMID 6890218. S2CID 41699283.
- ^ Mogg, K.; Bradley, B.P.; Miller, T.; Potts, H.; Glenwright, J.; Kentish, J. (1994). "Interpretation of homophones related to threat: Anxiety or response bias effects?". Cognitive Therapy and Research. 18 (5): 461–477. doi:10.1007/BF02357754. S2CID 36150769.
Sources edit
- Franklyn, Julian (1966). Which Witch? (1st ed.). New York, NY: Dorset Press. ISBN 0-88029-164-8.
- Room, Adrian (1996). An Alphabetical Guide to the Language of Name Studies. Lanham and London, UK: The Scarecrow Press. ISBN 978-081083169-8. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
- Stewart, Garrett (2015). The Deed of Reading: Literature, writing, language, philosophy. Ithaca, NY and London, UK: Cornell University Press. ISBN 978-150170170-2. Archived from the original on 14 April 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2020.
External links edit
- Homophone.com – a list of American homophones with a searchable database.
- Reed's homophones – a book of sound-alike words published in 2012
- Homophones.ml – a collection of homophones and their definitions
- Homophone Machine – swaps homophones in any sentence
- Useful tips ... English homophones – homophones list, activities and worksheets


