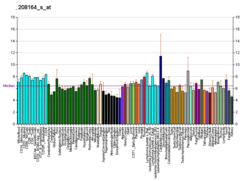
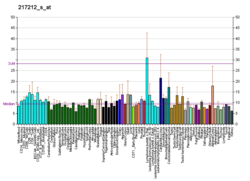
Summary
Interleukin 9 receptor (IL9R) also known as CD129 (Cluster of Differentiation 129) is a type I cytokine receptor. IL9R also denotes its human gene.[5]
| IL9R | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | IL9R, CD129, IL-9R, interleukin 9 receptor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 300007 MGI: 96564 HomoloGene: 37591 GeneCards: IL9R | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The protein encoded by this gene is a cytokine receptor that specifically mediates the biological effects of interleukin 9 (IL9). The functional IL9 receptor complex requires this protein as well as the interleukin 2 receptor, gamma (IL2RG), a common gamma subunit shared by the receptors of many different cytokines. The ligand binding of this receptor leads to the activation of various JAK kinases and STAT proteins, which connect to different biologic responses. This gene is located at the pseudoautosomal regions of X and Y chromosomes. Genetic studies suggested an association of this gene with the development of asthma. Multiple pseudogenes on chromosome 9, 10, 16, and 18 have been described. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.[5]
Interactions edit
Interleukin-9 receptor has been shown to interact with YWHAZ.[6]
See also edit
References edit
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000124334 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000020279 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: IL9R interleukin 9 receptor".
- ^ Sliva, D; Gu M; Zhu Y X; Chen J; Tsai S; Du X; Yang Y C (February 2000). "14-3-3zeta interacts with the alpha-chain of human interleukin 9 receptor". Biochem. J. 345 (3): 741–7. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3450741. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1220812. PMID 10642536.
Further reading edit
- Knoops L, Renauld JC (2005). "IL-9 and its receptor: from signal transduction to tumorigenesis". Growth Factors. 22 (4): 207–15. doi:10.1080/08977190410001720879. PMID 15621723. S2CID 40523692.
- Renauld JC, Druez C, Kermouni A, et al. (1992). "Expression cloning of the murine and human interleukin 9 receptor cDNAs". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89 (12): 5690–4. Bibcode:1992PNAS...89.5690R. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.12.5690. PMC 49358. PMID 1376929.
- Kimura Y, Takeshita T, Kondo M, et al. (1995). "Sharing of the IL-2 receptor gamma chain with the functional IL-9 receptor complex". Int. Immunol. 7 (1): 115–20. doi:10.1093/intimm/7.1.115. PMID 7718508.
- Chang MS, Engel G, Benedict C, et al. (1994). "Isolation and characterization of the human interleukin-9 receptor gene". Blood. 83 (11): 3199–205. doi:10.1182/blood.V83.11.3199.3199. PMID 8193355.
- Kermouni A, Van Roost E, Arden KC, et al. (1996). "The IL-9 receptor gene (IL9R): genomic structure, chromosomal localization in the pseudoautosomal region of the long arm of the sex chromosomes, and identification of IL9R pseudogenes at 9qter, 10pter, 16pter, and 18pter". Genomics. 29 (2): 371–82. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.9992. PMID 8666384.
- Demoulin JB, Uyttenhove C, Van Roost E, et al. (1996). "A single tyrosine of the interleukin-9 (IL-9) receptor is required for STAT activation, antiapoptotic activity, and growth regulation by IL-9". Mol. Cell. Biol. 16 (9): 4710–6. doi:10.1128/MCB.16.9.4710. PMC 231471. PMID 8756628.
- Vermeesch JR, Petit P, Kermouni A, et al. (1997). "The IL-9 receptor gene, located in the Xq/Yq pseudoautosomal region, has an autosomal origin, escapes X inactivation and is expressed from the Y". Hum. Mol. Genet. 6 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/6.1.1. PMID 9002663.
- Bauer JH, Liu KD, You Y, et al. (1998). "Heteromerization of the gammac chain with the interleukin-9 receptor alpha subunit leads to STAT activation and prevention of apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (15): 9255–60. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.15.9255. PMID 9535918.
- Levitt RC, McLane MP, MacDonald D, et al. (1999). "IL-9 pathway in asthma: new therapeutic targets for allergic inflammatory disorders". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 103 (5 Pt 2): S485–91. doi:10.1016/S0091-6749(99)70165-X. PMID 10329852.
- Sliva D, Zhu YX, Tsai S, et al. (1999). "Tip60 interacts with human interleukin-9 receptor alpha-chain". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 263 (1): 149–55. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1083. PMID 10486269.
- Sliva D, Gu M, Zhu YX, et al. (2000). "14-3-3zeta interacts with the alpha-chain of human interleukin 9 receptor". Biochem. J. 345 (3): 741–7. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3450741. PMC 1220812. PMID 10642536.
- Ciccodicola A, D'Esposito M, Esposito T, et al. (2000). "Differentially regulated and evolved genes in the fully sequenced Xq/Yq pseudoautosomal region". Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 (3): 395–401. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.3.395. PMID 10655549.
- De Smedt M, Verhasselt B, Kerre T, et al. (2000). "Signals from the IL-9 receptor are critical for the early stages of human intrathymic T cell development". J. Immunol. 164 (4): 1761–7. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.164.4.1761. PMID 10657622.
- Kauppi P, Laitinen T, Ollikainen V, et al. (2001). "The IL9R region contribution in asthma is supported by genetic association in an isolated population". Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 8 (10): 788–92. doi:10.1038/sj.ejhg.5200541. PMID 11039580.
- Abdelilah S, Latifa K, Esra N, et al. (2001). "Functional expression of IL-9 receptor by human neutrophils from asthmatic donors: role in IL-8 release". J. Immunol. 166 (4): 2768–74. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.166.4.2768. PMID 11160343.
- Asao H, Okuyama C, Kumaki S, et al. (2001). "Cutting edge: the common gamma-chain is an indispensable subunit of the IL-21 receptor complex". J. Immunol. 167 (1): 1–5. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.167.1.1. PMID 11418623.
- Little FF, Cruikshank WW, Center DM (2001). "Il-9 stimulates release of chemotactic factors from human bronchial epithelial cells". Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 25 (3): 347–52. doi:10.1165/ajrcmb.25.3.4349. PMID 11588013.
- Tsukadaira A, Okubo Y, Koyama S, et al. (2002). "Human bronchial epithelium expresses interleukin-9 receptors and releases neutrophil chemotactic factor". Exp. Lung Res. 28 (2): 123–39. doi:10.1080/019021402753462040. PMID 11868823. S2CID 26893804.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Melén E, Gullstén H, Zucchelli M, et al. (2005). "Sex specific protective effects of interleukin-9 receptor haplotypes on childhood wheezing and sensitisation". J. Med. Genet. 41 (12): e123. doi:10.1136/jmg.2004.023135. PMC 1735647. PMID 15591265.
External links edit
- IL9R+protein,+human at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.