
Summary
In geometry, the pentagrammic cuploid or pentagrammmic semicupola is the simplest of the infinite family of cuploids. It can be obtained as a slice of the small complex rhombicosidodecahedron. As in all cupolae, the base polygon has twice as many edges and vertices as the top; but in this case the base polygon is a degenerate {10/2} decagram, as the top is a {5/2} pentagram. Hence, the degenerate base is withdrawn and the triangles are connected to the squares instead.
| Pentagrammic cuploid | |
|---|---|
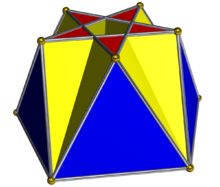 | |
| Type | Cuploid |
| Faces | 5 triangles 5 squares 1 pentagram |
| Edges | 20 |
| Vertices | 10 |
| Vertex configuration | 5(5/2.4.3.4) 5(3.4.3/2.4/3) |
| Symmetry group | C5v, [5], (*55) |
| Rotation group | C5, [5]+, (55) |
| Dual polyhedron | Pentagrammic keratinoid |
| Properties | non-orientable has a membrane |

Related polyhedra edit
| n⁄d | 3 | 5 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | {3/2} Crossed triangular cuploid |
{5/2} Pentagrammiccuploid {7/2} Heptagrammic cuploid | |
| 4 | — | {5/4} Crossed pentagonal cuploid |
{7/4} Crossed heptagrammic cuploid |
The pentagrammic cuploid may be seen as a section of the degenerate uniform polyhedron known as the small complex rhombicosidodecahedron:
| Pentagrammic cuploid |
Small complex rhombicosidodecahedron | ||
| Small ditrigonal icosidodecahedron |
Ditrigonal dodecadodecahedron |
Great ditrigonal icosidodecahedron |
Compound of five cubes |
(In the picture of the pentagrammic cuploid, the pentagram is red, the squares yellow, and the triangles blue. In the picture of the small complex rhombicosidodecahedron, the pentagrams are pink, the squares red, and the triangles yellow. The centres of the pentagrams have been removed as otherwise the red squares of the small complex rhombicosidodecahedron would be invisible.)
Taking one pentagram from the small complex rhombicosidodecahedron, then taking the five squares that neighbour it, then taking the five triangles that border these squares results in a pentagrammic cuploid. As this pentagrammic cuploid thus shares all its edges with this polyhedron, it may be termed an edge-faceting of it. The nondegenerate uniform polyhedra sharing the same edges as the small complex rhombicosidodecahedron are the three ditrigonal polyhedra, as well as the regular compound of five cubes: hence the pentagrammic cuploid is also an edge-faceting of these polyhedra.
As 5/2 > 2, the triangles and squares do not fully cover the bottom of the pentagrammic cuploid, and hence the centre of the pentagrammic base is accessible from both sides and covers no space. Hence it is a membrane and has not been filled in in the above illustration of the polyhedron, as filling it in would imply that the densities on either of the pentagram are different, when they are both 0. It has been conjectured that a polyhedron with 10 faces or less cannot have a membrane: the pentagrammic cuploid has 11 faces.
Dual polyhedron edit
The dual of the pentagrammic cuploid has 5 kite and 5 antiparallelogram faces, and has been called the pentagrammic keratinoid by Inchbald, due to it being shaped like a hollow horn:
References edit
- Guy Inchbald, Filling polytopes
- Richard Klitzing, Axial-Symmetrical Edge Facetings of Uniform Polyhedra
- Richard Klitzing, Facetings of uniform polyhedra (hosted and presented by Ulrich Mikloweit)
- Jim McNeill, The 5/2 semicupola and 5/4 semicupola
- Jim McNeill, Semicupolas


