
Summary
A total solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, July 22, 2028. The central line of the path of the eclipse will cross the Australian continent from the Kimberley region in the north-west and continue in a south-easterly direction through Western Australia, the Northern Territory, south-west Queensland and New South Wales, close to the towns of Wyndham, Kununurra, Tennant Creek, Birdsville, Bourke and Dubbo, and continuing on through the centre of Sydney, where the eclipse will have a duration of over three minutes. It will also cross Queenstown and Dunedin, New Zealand. Totality will also be viewable from two of Australia's external territories: Christmas Island and the Cocos (Keeling) Islands.
| Solar eclipse of July 22, 2028 | |
|---|---|
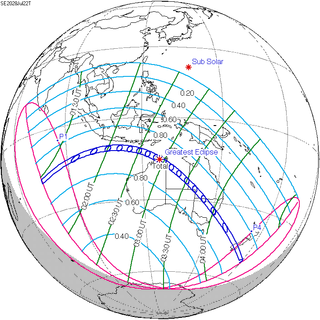 Map | |
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.6056 |
| Magnitude | 1.056 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 310 s (5 min 10 s) |
| Coordinates | 15°36′S 126°42′E / 15.6°S 126.7°E |
| Max. width of band | 230 km (140 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 2:56:40 |
| References | |
| Saros | 146 (28 of 76) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9570 |

This is the first time Sydney will experience a total solar eclipse since March 26, 1857 and will be the last until June 3, 2858.[1]
Related eclipses edit
Eclipses in 2028 edit
- A partial lunar eclipse on Wednesday, 12 January 2028.
- An annular solar eclipse on Wednesday, 26 January 2028.
- A partial lunar eclipse on Thursday, 6 July 2028.
- A total solar eclipse on Saturday, 22 July 2028.
- A total lunar eclipse on Sunday, 31 December 2028.
Solar eclipses of 2026–2029 edit
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 121 | 2026 February 17 Annular |
−0.97427 | 126 | 2026 August 12 Total |
0.89774 | |
| 131 | 2027 February 6 Annular |
−0.29515 | 136 | 2027 August 2 Total |
0.14209 | |
| 141 | 2028 January 26 Annular |
0.39014 | 146 | 2028 July 22 Total |
−0.60557 | |
| 151 | 2029 January 14 Partial |
1.05532 | 156 | 2029 July 11 Partial |
−1.41908 | |
Partial solar eclipses on June 12, 2029, and December 5, 2029, occur in the next lunar year eclipse set.
Tzolkinex edit
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of June 10, 2021
- Followed: Solar eclipse of September 12, 2034
Tritos edit
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of August 21, 2017
- Followed: Solar eclipse of June 21, 2039
Saros 146 edit
It is a part of Saros cycle 146, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 76 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on September 19, 1541. It contains total eclipses from May 29, 1938, through October 7, 2154, hybrid eclipses from October 17, 2172, through November 20, 2226, and annular eclipses from December 1, 2244, through August 10, 2659. The series ends at member 76 as a partial eclipse on December 29, 2893. The longest duration of totality was 5 minutes, 21 seconds on June 30, 1992.
| Series members 21-37 occur between 1901 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 21 | 22 | 23 |
| May 7, 1902 |
May 18, 1920 |
May 29, 1938 |
| 24 | 25 | 26 |
| June 8, 1956 |
June 20, 1974 |
June 30, 1992 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 |
| July 11, 2010 |
July 22, 2028 |
August 2, 2046 |
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
| August 12, 2064 |
August 24, 2082 |
September 4, 2100 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
| September 15, 2118 |
September 26, 2136 |
October 7, 2154 |
| 36 | 37 | |
| October 17, 2172 |
October 29, 2190 | |
Metonic cycle edit
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 events between July 22, 1971 and July 22, 2047 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| July 21–22 | May 9–11 | February 26–27 | December 14–15 | October 2–3 |
| 116 | 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 |
| July 22, 1971 |
May 11, 1975 |
February 26, 1979 |
December 15, 1982 |
October 3, 1986 |
| 126 | 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 |
| July 22, 1990 |
May 10, 1994 |
February 26, 1998 |
December 14, 2001 |
October 3, 2005 |
| 136 | 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 |
| July 22, 2009 |
May 10, 2013 |
February 26, 2017 |
December 14, 2020 |
October 2, 2024 |
| 146 | 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 |
| July 22, 2028 May 9, 2032 |
February 27, 2036 |
December 15, 2039 |
October 3, 2043 | |
| 156 | ||||
| July 22, 2047 | ||||
References edit
- ^ Espenak, Fred. "Major Solar Eclipses visible from Sydney, Australia". NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
External links edit
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Google interactive map
- Besselian elements


